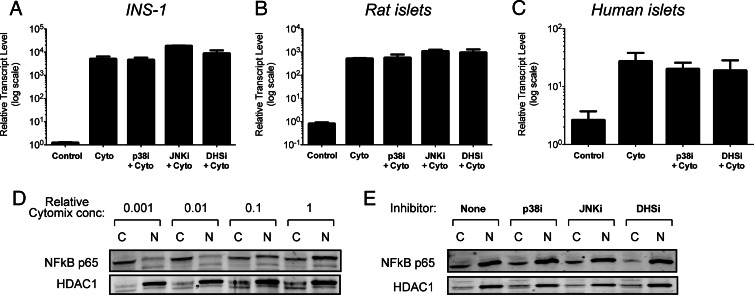
Fig. 2.
Effects of enzyme inhibitors on cytokine-induced Nos2 gene activation and NFκB nuclear translocation. INS-1 β cells (A[b]), rat islets (B[b]), and human islets (C[b]) were untreated (Control) or exposed to a standard cytomix concentration for 4 h, with or without indicated inhibitors, then cells were harvested for RNA isolation and real-time RT-PCR was performed for Nos2 message. In panels A–C, data are corrected for Actb message levels, and then normalized to Nos2 message levels in the absence of cytomix (Control). D, INS-1 cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of cytomix for 4 h, and then cytoplasmic (“C”) and nuclear (“N”) extracts were isolated and subjected to immunoblotting for NFκB p65 subunit and HDAC1 (nuclear protein control). E, INS-1 cells were exposed to a standard cytomix concentration, with or without indicated inhibitors, and then cytoplasmic (“C”) and nuclear (“N”) extracts were isolated and subjected to immunoblotting for NFκB p65 subunit and histone deacetylase (HDAC)1 (nuclear protein control). Panels A[b]–C represent the mean ± sem]r] of triplicate determinations from at least three independent experiments, and panels D and E are representative of experiments performed on three separate occasions. JNKi, 10 μ[scap]m JNK inhibitor SP600125; p38i and DHSi are as indicated in the legend to Fig. 1.