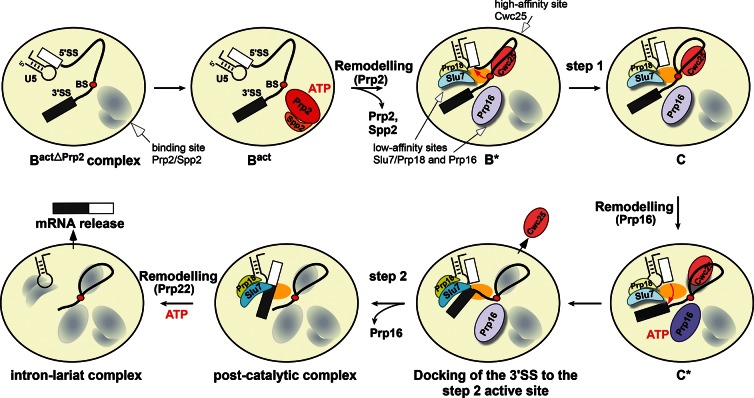
FIGURE 6.
Binding and activity of step 1 and step 2 factors during the catalytic phase of the spliceosome. Schematic representation of the substantial remodeling that the precatalytic Bact spliceosome undergoes during the transition from step 1 to step 2 catalysis. The ATPases Prp2 and Prp16 are required for activating the spliceosome for the first and second catalytic steps, respectively. The ATPase Prp2 plus ATP creates a high-affinity binding site for Cwc25, which stabilizes the step 1 conformation of the catalytic center, thereby facilitating step 1 catalysis. Prp2 also creates low-affinity binding sites for Prp16 and Slu7; the latter binds to the spliceosome only together with Prp18. The ATPase Prp16 plus ATP is required for remodeling the spliceosome for step 2 catalysis and to stabilize the binding of Slu7/Prp18, which is needed to dock efficiently the 3′SS into the step 2 active site, leading to displacement of Cwc25 before exon ligation. The exons are then ligated and the post-catalytic spliceosome is generated. Proteins are oval-shaped, shadowed, and highlighted with light colors (low binding affinity) or with dark colors without a shadow (high binding affinity). The yellow oval in the middle of the spliceosome represents the active site. The conserved U5 stem–loop I is also shown.