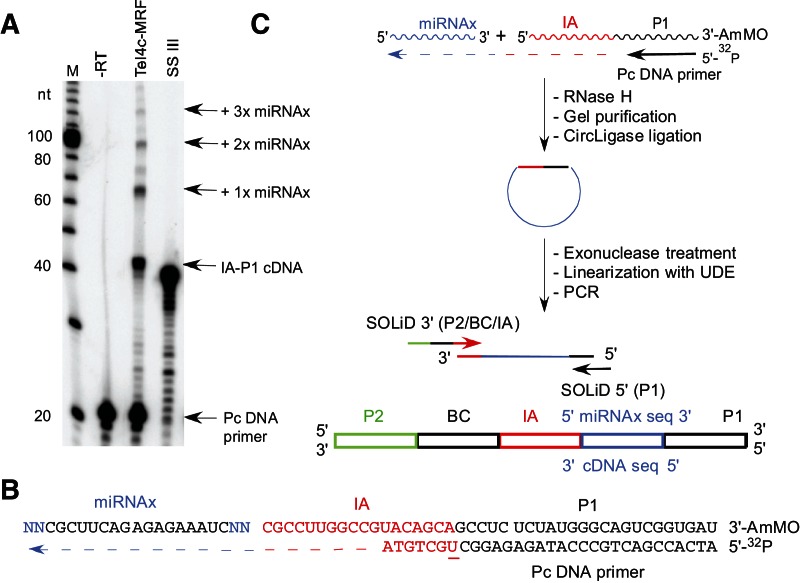
FIGURE 6.
Template-switching activity of group II intron and retroviral RTs. (A) Gel assay. The initial 32P-labeled IA–P1 RNA/Pc DNA template-primer substrate (50 nM) and equimolar miRNAx were incubated with TeI4c-MRF RT (2 μM, 60°C) or SuperScript III (10 units/μL, 50°C; SSIII) for 15 min in the standard reaction medium for each enzyme (see Materials and Methods). The products were analyzed in a denaturing 20% polyacrylamide gel, which was scanned with a PhosphorImager. Lane “−RT” shows the IA–P1 RNA/Pc DNA substrate incubated under TeI4c-MRF RT conditions without RT. (Lane M) 32P-labeled 10-bp ladder size markers. (B) Template and primer sequences. The miRNAx target RNA has two randomized nucleotide residues (NN; blue) at each end to assess template-switching biases (Supplemental Fig. S4). The initial IA–P1 template RNA has a 3′ aminomodifier (AmMO) to impede template switching to that RNA end, and the Pc DNA primer is 5′ 32P-labeled and has an internal deoxyuridine (underlined) for relinearization of cDNAs after circularization with uracil–DNA excision mix (UDE; see below). (C) Protocol for the construction of cDNA libraries via group II intron RT template switching. In the first step, the group II intron RT template switches from the IA–P1 RNA/Pc DNA template/primer to miRNAx to generate a continuous cDNA that links the IA–P1 adaptor sequence to that of miRNAx. The products are then incubated with RNase H to digest the RNA template, gel-purified, and circularized with CircLigase. After digestion of unincorporated primers with exonuclease I, the cDNAs were relinearized with UDE at the deoxyuridine in the primer and amplified by PCR with primers that append adaptors and barcodes for next-generation sequencing.