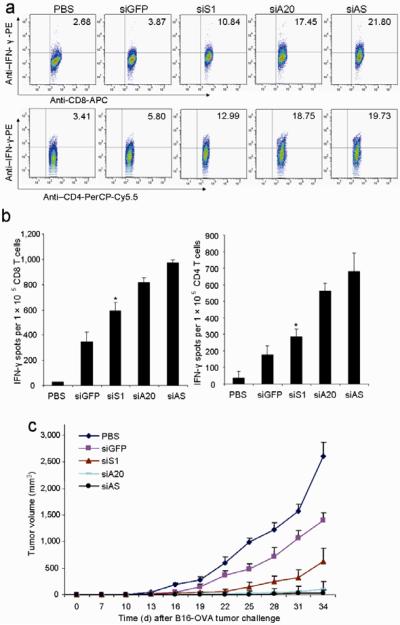
Figure 4. Comparison of antitumor activity with siS1-DCs.
a&b. Intracellular IFN-γ staining and ELISPOT assays. C57BL/6 mice were immunized once with OVA-pulsed, LV-transduced DCs ex vivo matured with LPS followed by in vivo stimulation with polyI:C (i.p.) once. Lymphocytes of pooled draining LN from immunized mice were subjected to intracellular staining after 4 hr in vitro restimulation (a). CD8+ T cells or CD4+ T cells isolated from pooled splenocytes of immunized mice were subjected to IFNγ ELISPOT assays (b). Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. *P < 0.05, siS1-DC vs. siA20-DC.
c. Antitumor activity against pre-established tumors. Groups of C57BL/6 mice were inoculated s.c. with B16-OVA tumor cells (2.5×105) and five days later, were immunized via the rear footpad with 1 ×106 OVA-pulsed, LV-transduced DCs with ex vivo LPS maturation (100 ng/ml). One day after DC transfer, in vivo polyI:C was administered i.p. once. Tumor growth curves (n=6 mice/group) represent one of three independent experiments. P < 0.05, siS1-DC compared with siA20-DC mice.