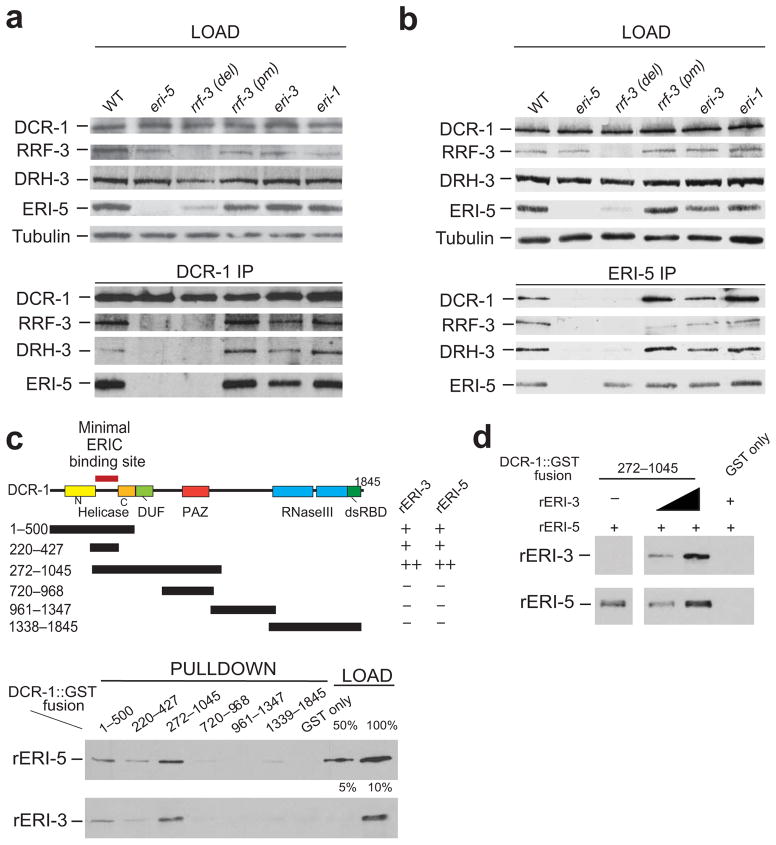
Figure 2. ERI-5 promotes the association of an RdRP module to DCR-1 N-terminus.
(a, b) IP of DCR-1 and ERI-5 in WT, eri-5, rrf-3 del (deletion mutant, pk1426), rrf-3 pm (point mutant, mg373), eri-3 and eri-1 mutant embryos. DCR-1, RRF-3, DRH-3 and ERI-5 were detected by western blot. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (c) (top) Map of the DCR-1-GST constructs used for the GST pull-down of recombinant (r) ERI-5 or ERI-3. The ability of each DCR-1-GST fusion to interact with rERI-5 or rERI-3 was assessed by western blot (bottom panel) to detect recombinant rERI-5-CBP or rERI-3-FLAG. The results are summarized to the right of the DCR-1 map; “−” denotes weak or no interaction, “+” denotes an interaction. (see Supplementary Fig. 2c for Coomassie Blue gel staining). Percentage (%) of the loading (bottom panel) represents the fraction of rERI-5 and rERI-3 used in the GST pull-down. (d) ERI-3 and ERI-5 bind to DCR-1(272–1045) simultaneously. An increasing amount of rERI-3 was pre-incubated with DCR-1(272–1045) prior to addition of rERI-5 and pull-down of the DCR-1 fragment.