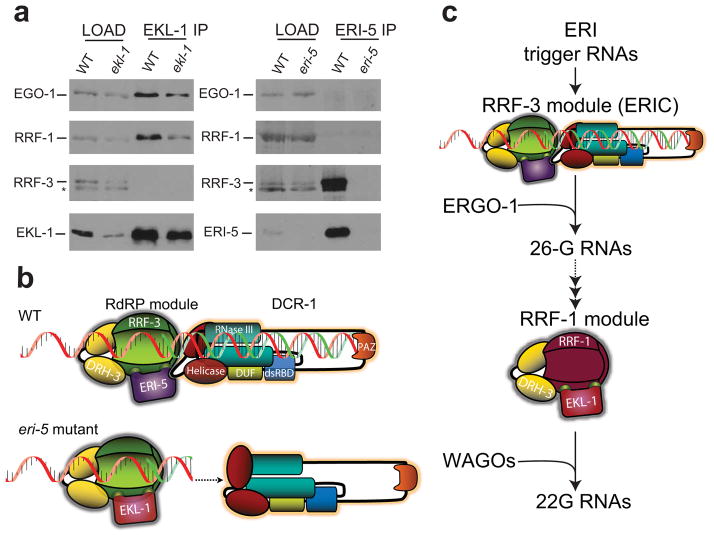
Figure 5. Roles and paralog organization of RdRP modules in ERI endo-RNAi.
(a) IP of EKL-1 in WT and ekl-1(RNAi) (ekl-1 lanes) embryos, and IP of ERI-5 in WT and eri-5 mutant embryos. The RdRPs EGO-1, RRF-1, RRF-3, and the tudor domain EKL-1 and ERI-5 proteins were detected by western blot. Asterisk (*) indicates a non-specific band. (b) Model of the molecular compensation of ERI-5 by EKL-1. Interactions between the RdRP module and the N-terminal helicase domain of DCR-1 couple the generation of dsRNA by RRF-3 with processive DCR-1 activity. In the eri-5 mutant, this coupling is lost and the auto-inhibitory function of the helicase domain predominates, resulting in inefficient 26-G-RNA production. (c) Paralogous RdRP modules function sequentially in ERI endo-RNAi. An RdRP module comprised of RRF-3, DRH-3 and ERI-5 together with DCR-1 function at the initial step to generate 26-G-RNAs, the primary siRNAs of the ERI pathway that program ERGO-1. A paralogous RdRP module comprised of RRF-1, DRH-3 and EKL-1 is responsible for secondary siRNA generation that is independent of DCR-1. This abundant pool of small RNAs programs the WAGO Argonautes to effect endo-RNAi silencing. Paralogous EGO-1 complexes may be involved in this and other RNAi pathways. Some of the ERIC components were omitted from the model for clarity.