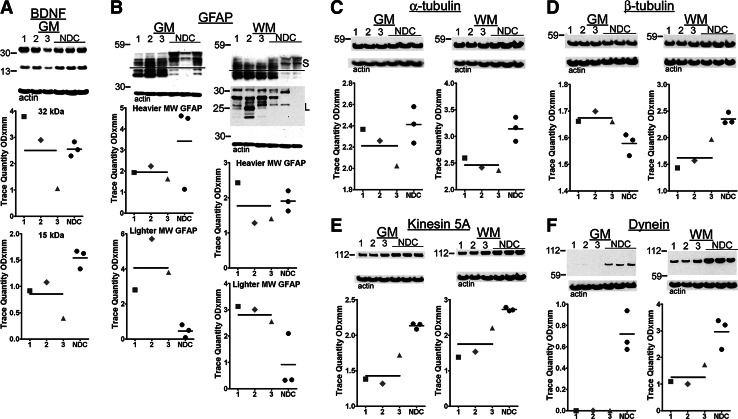
FIG. 6.
Western blots from gray matter brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM) glial acidic fibrillary protein (GFAP), α-tubulin, β-tubulin, kinesin 5A, and dynein. (A) The average amounts of the active form of the BDNF (∼15 kDa) were decreased in the dementia pugilistica (DP) cases when compared with the non-demented controls (NDC). (B) The GFAP demonstrated a substantive quantitative increase of lighter molecular weight isoforms in the DP persons relative to NDC and different banding patterns as well as a large amount of degraded GFAP on a longer exposure time. For the purposes of quantification, we arbitrarily divided the GFAP pattern into two different groups as indicated by the horizontal line. Relative to the NDC average levels: (C) the mean α-tubulin was decreased in both GM and WM; (D) the β-tubulin was increased in the GM and decreased in the WM. Larger deviations were found in the cargo proteins, (E) kinesin 5A mean values were decreased in the GM and WM, (F) the dynein mean levels were also decreased, to values below the level of detection by Western blot analysis in GM and more modestly in WM. See Figure 2 for shape codes and Western blot notes. MW, molecular weight; S, short exposure; L, long exposure.