Table 1.
Optimization of reaction conditions.a
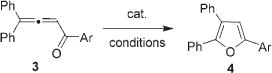
| Entry | Catalystb | mol% | Solvent | T [°C] | Yield [%]c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AuBr3 | 5 | toluened | 100 | 23 |
| 2 | AuI | 5 | toluened | 100 | traces |
| 3 | [Au(PPh3)]OTf | 1 | toluened | 100 | 100 (89) |
| 4 | [Au(PPh3)]OTf | 5 | CH2Cl2e | RT | 99 |
| 5 | PtCl2 | 5 | toluenef | 100 | 21 |
| 6 | PtCl4 | 5 | toluenef | 100 | 21 |
| 7 | [PdCl2(PhCN)2] | 5 | toluenef | 100 | 35 |
| 8 | CuX (X = Cl, Br, I) | 5 | toluenef | 100 | 0 |
| 9 | CuOTf·PhH | 5 | toluenef | 100 | 42 |
| 10 | Cu(OTf)2 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 95 |
| 11 | AgPF6 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 47 |
| 12 | AgOTf | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | (80) |
| 13 | AgOTf | 20 | CH2Cl2e | RT | 70 (62) |
| 14 | Al(OTf)3 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 64 |
| 15 | Zn(OTf)2 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 39 |
| 16 | TMSOTf | 20 | CH2Cl2e | RT | 82 (62) |
| 17 | In(OTf)3 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 91 (81) |
| 18 | Sn(OTf)2 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 97 (81) |
| 19 | TIPSOTf | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 100 (81) |
| 20 | TMSNTf2 | 5 | tolueneg | 100 | 72 |
Entries 1–4: Ar = p-Br-C6H4; entries 5–20: Ar = Ph.
Tf = trifluoromethanesulfonyl, TIPS = triisopropylsilyl, TMS = trimethylsilyl.
Yield determined from NMR spectrum; yield of isolated product in parentheses.
0.05 M, solution of 3.
0.02 M solution of 3.
1 M solution of 3.
0.1 M solution of 3.
