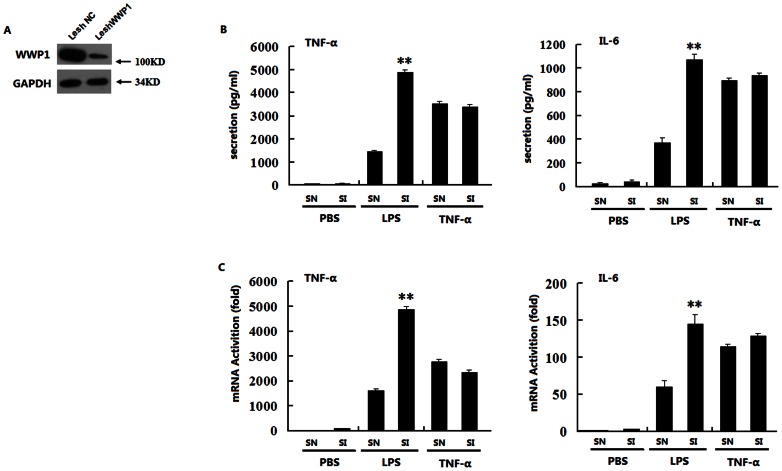
Figure 1. Knocking down WWP1 enhances TNF-α and IL-6 production induced by LPS but not by TNF-α.
(A) Effects of WWP1 RNAi (Lesh WWP1) on WWP1 expression. Peritoneal macrophages (2×106) were infected with the Lesh NC and Lesh WWP1 virus particles (m.o.i 40) for 48 h, and immunoblot analysis was then performed with the anti-WWP1 antibody. (B) Effects of WWP1 RNAi (Lesh WWP1) on LPS or TNF-α–induced TNF-α and IL-6 secretion. Peritoneal macrophages (7.5×105) were infected with the Lesh NC and Lesh WWP1 virus particles (m.o.i 40) for 48 h, and then, LPS (at a final concentration of 400 ng/mL) or TNF-α (at a final concentration of 10 ng/mL) was used to stimulate the cells. The medium was changed 60 minutes later to fresh DMEM with 10% FBS, and ELISA analysis was used to detect TNF-α and IL-6 secretion after 12 h of stimulation. (C) Effects of WWP1 RNAi (Lesh WWP1) on LPS or TNF-α induced TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA transcription. Peritoneal macrophages (7.5×105) were infected with the Lesh NC and Lesh WWP1 virus particles (m.o.i 40) for 48 h, and then, LPS (at a final concentration of 400 ng/mL) or TNF-α (at a final concentration of 10 ng/mL) were added to stimulate the cells for 8 h respectively. RT-PCR analysis was used to detect TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA levels. **P<0.01 (t-test), data are representative of three independent experiments (mean and S.D. of three replicates).