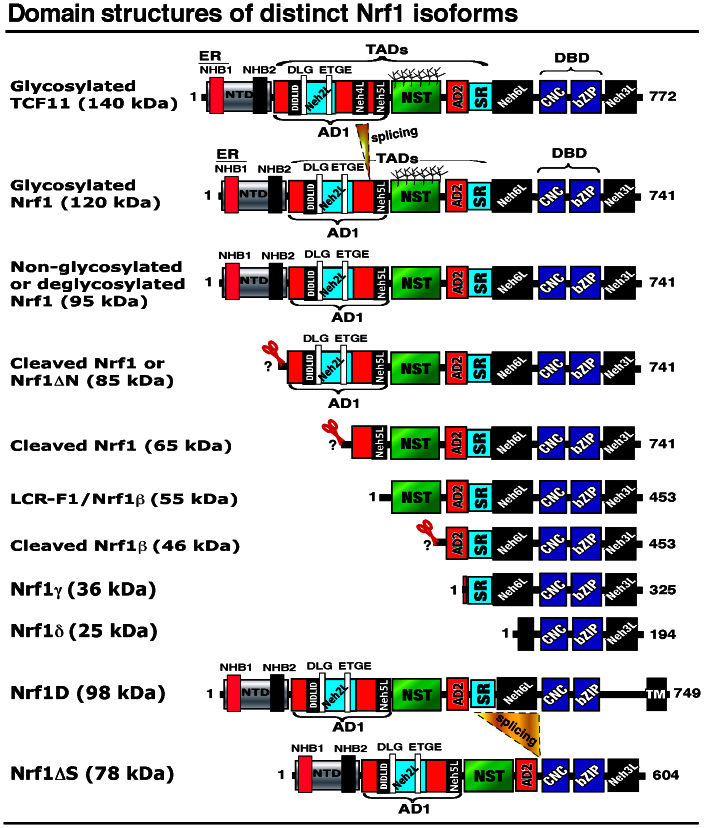
Figure 1. Structural domains of distinct Nrf1 isoforms.
The N-terminal domain (NTD) contains a TM1-associated NHB1 sequence that dictates Nrf1 to target to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and enables it to anchor within the membrane. Both CNC and bZIP regions were combined into the Neh1L (Nrf2-ECH homology 1-like) domain that enables heterodimerization with a small Maf or other bZIP proteins before binding to antioxidant response element (ARE) sequences in the promoter regions of target genes. The transactivation domains (TADs) of Nrf1 comprise AD1 (acidic domain 1), NST (Asn/Ser/Thr-rich), AD2 and SR (serine-repeat) regions. On the C-terminal border of NST glycodomain immediately to the acidic-hydrophobic amphipathic AD2, the TMi segment may act as a luminal-anchoring switch to control repartitioning of its flanking AD1 and AD2/SR domains. Within AD1, Neh2L contains the DIDLID/DLG element and ETGE motif; both are conserved with equivalents of Nrf2 and CncC. In addition to Neh2L, the Neh5L, but not Neh4L, subdomain is included within AD1 of Nrf1, when compared with its longer TCF11. The N-linked glycosylation of the NST domain confers Nrf1 and TCF11 to migrate electrophoretically at estimated masses of ∼120-kDa and ∼140-kDa, respectively, whilst their non-glycosylated/deglycosylated proteins exhibit fast electrophoretic mobilities at ∼95-kDa and ∼110-kDa. They may be further processed through selective proteolysis to give rise to multiple cleaved forms of between 85-kDa and 25-kDa. Of which the putative activated 85-kDa protein can be also translated through an alternative initiation signal (in Nrf1 Δ767 clones designated originally51,52) so that it lacks an ER-anchoring NTD (thus called Nrf1ΔN), and may be further processed into an unstable polypeptide of 65-kDa or 55-kDa. The 55-kDa form, that was originally designated LCR-F1 (called Nrf1β herein), is produced by in-frame translation and/or selective proteolysis, and may be rapidly degraded to yield short dominant-negative isoforms of 46-kDa, 36-kDa (called Nrf1γ) and 25-kDa (called Nrf1δ). For convenience, Nrf1 variant ΔD and Δ10 clones51,52 are renamed as Nrf1D or Nrf1ΔS, respectively. The triangle represents a loss of the corresponding region by alternative splicing, whereas the scissors with a question mark (?) indicate unidentified cleavage sites.