Abstract
In the title compound, C13H8Cl3NO4S, the aromatic rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 68.94 (1)° and the molecule adopts a V-shape. An intramolecular N—H⋯O interaction generates a six-membered S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, pairs of O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving the carboxy group link the molecules into inversion dimers with an R 2 2(8) motif. N—H⋯O and non-classical C—H⋯O interactions connect the molecules, forming sheets propagating in (100).
Related literature
For the synthesis, see: Arshad et al. (2012 ▶) For related structures, see: Arshad et al. (2009 ▶, 2011 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H8Cl3NO4S
M r = 380.61
Monoclinic,

a = 9.0164 (3) Å
b = 18.6017 (5) Å
c = 9.8574 (3) Å
β = 111.653 (3)°
V = 1536.62 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 6.83 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.38 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova (Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas, CCD) diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.467, T max = 1.000
11742 measured reflections
3018 independent reflections
2597 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.104
S = 1.04
3018 reflections
201 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.60 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011574/hg5312sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011574/hg5312Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011574/hg5312Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O3 | 0.86 | 2.55 | 2.940 (2) | 108 |
| C12—H12⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.425 (3) | 150 |
| O3—H3⋯O4ii | 0.82 | 1.85 | 2.666 (2) | 176 |
| N1—H1⋯O2iii | 0.86 | 2.30 | 3.128 (2) | 162 |
| C5—H5⋯O4iv | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.256 (4) | 135 |
| C10—H10⋯O1v | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.165 (3) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Abdulaziz University for the support of this research via the Research Group Track of Grant No. (3-102/428).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In connection to synthesis of halogenated sulfonamide derivatives 2-Chloro-4-(2-iodobenzenesulfonamido)benzoic acid (Arshad et al., 2011) and 2-Chloro-5-(2-iodobenzenesulfonamido)benzoic acid (Arshad et al., 2009), we are reporting the crystal structure of title compound.
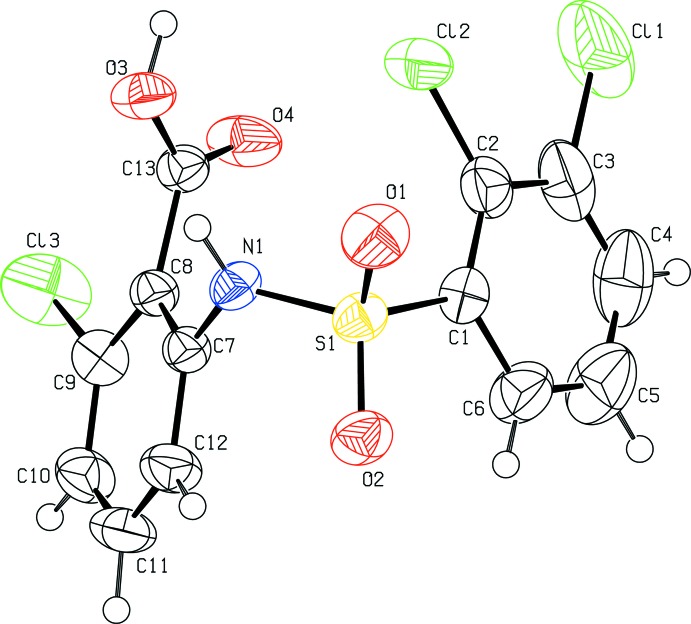
The two aromatic rings [(C1—C6) & (C7—C12)] in the structure of molecule are oriented at dihedral angle of 68.94 (1)°. The carboxylic group (C13/O3/O4) is twisted at 58.11 (1)° with respect to its mother aromatic ring (C7—C12) and its atoms C13, O3 & O4 are away by -0.1938 (35)Å , 0.6924 (39)Å , -1.1739 (39)Å repectively from the mean plane generating from atoms C7/C8/C9/C10/C11/C12 with the r.m.s deviation of 0.0183 (15) Å. The amino and carboxylic groups are involved in classical N1—H1···O3 intramolecular hydrogen bonding interaction and produce six membered ring motif S11 (6) (Bernstein et al. 1995) which is oriented at dihedral angles of 54.30 (11)° & 18.98 (12)° with respect to two aromatic rings [(C1—C6) & (C7—C12)], respectively. On the other hand the amino group get connected with oxygen of SO2 to form intermolecular N1—H1···O2 hydrogen bond. The carboxylic group gives typical inversion dimerization by generating eight membered ring motif R22 (8) (Bernstein et al. 1995) through O3—H3···O4 interaction. The non-clasical C—H···O type interaction have also been observed in the molecule (Fig. 2) for which symmetry detail are available in Table 1.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesised following the literature method (Arshad et al., 2012) and recrystallized from ethylacetate under slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
All the H-atoms were positioned with idealized geometry with C—H = 0.93 Å, N—H = 0.86 Å, O—H = 0.82 Å and were refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(K), where K = C, N & O for all H-atoms. The reflections (0 1 2), (1 3 1), (1 0 0), (2 1 0) & (0 2 0) are omitted in final refinement.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The labelled structure of (C13 H8 Cl3 N O4 S) with 50% probability of thermal ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
A perspective view showing two dimensional network generating through O—H···O, N—H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds, drawn using dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C13H8Cl3NO4S | F(000) = 768 |
| Mr = 380.61 | Dx = 1.645 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 5339 reflections |
| a = 9.0164 (3) Å | θ = 4.8–73.0° |
| b = 18.6017 (5) Å | µ = 6.83 mm−1 |
| c = 9.8574 (3) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 111.653 (3)° | Prismatic, colorless |
| V = 1536.62 (8) Å3 | 0.38 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova (Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas, CCD) diffractometer | 3018 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 2597 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.025 |
| ω scans | θmax = 73.1°, θmin = 5.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | h = −10→11 |
| Tmin = 0.467, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −22→22 |
| 11742 measured reflections | l = −12→11 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.104 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0471P)2 + 1.0131P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3018 reflections | Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3 |
| 201 parameters | Δρmin = −0.60 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0022 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.21203 (15) | 0.41272 (5) | 0.58195 (14) | 0.1161 (5) | |
| Cl2 | 0.17428 (9) | 0.55156 (5) | 0.74492 (8) | 0.0718 (3) | |
| Cl3 | 0.94473 (9) | 0.58369 (5) | 1.01517 (11) | 0.0797 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.24536 (6) | 0.70690 (3) | 0.62789 (6) | 0.03763 (17) | |
| O1 | 0.1045 (2) | 0.71147 (11) | 0.6596 (2) | 0.0562 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.2792 (2) | 0.76184 (9) | 0.54279 (18) | 0.0482 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.5137 (2) | 0.59728 (8) | 1.02304 (19) | 0.0460 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.4816 | 0.5600 | 1.0473 | 0.055* | |
| O4 | 0.6012 (2) | 0.52066 (9) | 0.8971 (2) | 0.0572 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.3928 (2) | 0.70318 (10) | 0.78616 (19) | 0.0357 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.3706 | 0.7032 | 0.8638 | 0.043* | |
| C1 | 0.2524 (3) | 0.62421 (13) | 0.5405 (2) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.2255 (3) | 0.55805 (14) | 0.5932 (3) | 0.0510 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.2403 (4) | 0.49629 (16) | 0.5195 (4) | 0.0693 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.2779 (4) | 0.5009 (2) | 0.3962 (4) | 0.0843 (11) | |
| H4 | 0.2867 | 0.4592 | 0.3476 | 0.101* | |
| C5 | 0.3022 (5) | 0.5663 (2) | 0.3450 (4) | 0.0804 (10) | |
| H5 | 0.3269 | 0.5691 | 0.2615 | 0.096* | |
| C6 | 0.2903 (4) | 0.62797 (17) | 0.4168 (3) | 0.0583 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.3078 | 0.6724 | 0.3823 | 0.070* | |
| C7 | 0.5563 (2) | 0.69989 (11) | 0.8019 (2) | 0.0327 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.6539 (2) | 0.64427 (11) | 0.8821 (2) | 0.0329 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.8156 (3) | 0.64584 (13) | 0.9024 (3) | 0.0418 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.8775 (3) | 0.69735 (14) | 0.8382 (3) | 0.0485 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.9852 | 0.6970 | 0.8518 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | 0.7777 (3) | 0.74919 (15) | 0.7535 (3) | 0.0536 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.8175 | 0.7829 | 0.7061 | 0.064* | |
| C12 | 0.6188 (3) | 0.75223 (13) | 0.7376 (3) | 0.0467 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.5540 | 0.7892 | 0.6840 | 0.056* | |
| C13 | 0.5870 (3) | 0.58240 (11) | 0.9374 (2) | 0.0348 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.1280 (9) | 0.0446 (5) | 0.1266 (9) | −0.0192 (5) | −0.0106 (7) | 0.0082 (5) |
| Cl2 | 0.0734 (5) | 0.0782 (5) | 0.0597 (4) | −0.0271 (4) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.0177 (4) |
| Cl3 | 0.0502 (4) | 0.0720 (5) | 0.1115 (7) | 0.0207 (3) | 0.0236 (4) | 0.0361 (5) |
| S1 | 0.0363 (3) | 0.0420 (3) | 0.0365 (3) | 0.0046 (2) | 0.0158 (2) | 0.0039 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0388 (9) | 0.0760 (13) | 0.0587 (11) | 0.0094 (8) | 0.0238 (8) | 0.0034 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0531 (9) | 0.0456 (10) | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0048 (7) | 0.0153 (7) | 0.0123 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0692 (11) | 0.0324 (8) | 0.0514 (10) | −0.0026 (8) | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0004 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0914 (14) | 0.0287 (8) | 0.0748 (13) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0580 (11) | −0.0055 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0380 (9) | 0.0422 (10) | 0.0303 (9) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0419 (11) | 0.0449 (13) | 0.0356 (11) | −0.0006 (10) | 0.0111 (9) | −0.0023 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0446 (13) | 0.0496 (15) | 0.0468 (14) | −0.0081 (11) | 0.0027 (11) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0639 (17) | 0.0444 (16) | 0.072 (2) | −0.0044 (13) | −0.0075 (15) | −0.0037 (14) |
| C4 | 0.095 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0129 (19) | 0.0098 (19) | −0.0296 (18) |
| C5 | 0.108 (3) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0594 (19) | 0.012 (2) | 0.0362 (19) | −0.0156 (17) |
| C6 | 0.0753 (18) | 0.0590 (17) | 0.0460 (14) | 0.0016 (14) | 0.0285 (13) | −0.0020 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0369 (10) | 0.0302 (10) | 0.0325 (10) | −0.0020 (8) | 0.0148 (8) | −0.0012 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0270 (10) | 0.0336 (10) | −0.0026 (8) | 0.0166 (8) | −0.0021 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0396 (11) | 0.0391 (12) | 0.0474 (13) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0168 (10) | 0.0002 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0556 (15) | 0.0568 (15) | −0.0089 (10) | 0.0218 (11) | −0.0030 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0518 (14) | 0.0530 (16) | 0.0602 (16) | −0.0145 (11) | 0.0257 (12) | 0.0121 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0468 (13) | 0.0401 (13) | 0.0515 (14) | −0.0042 (10) | 0.0161 (11) | 0.0126 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0418 (11) | 0.0297 (10) | 0.0357 (11) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0174 (9) | 0.0012 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C3 | 1.725 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.366 (5) |
| Cl2—C2 | 1.725 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| Cl3—C9 | 1.724 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.373 (4) |
| S1—O1 | 1.4179 (17) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| S1—O2 | 1.4247 (17) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| S1—N1 | 1.6357 (18) | C7—C12 | 1.389 (3) |
| S1—C1 | 1.776 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.399 (3) |
| O3—C13 | 1.279 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.397 (3) |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | C8—C13 | 1.493 (3) |
| O4—C13 | 1.238 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.375 (3) |
| N1—C7 | 1.426 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.372 (4) |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.384 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.391 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.391 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (5) | ||
| O1—S1—O2 | 119.37 (11) | C5—C6—C1 | 120.3 (3) |
| O1—S1—N1 | 105.73 (10) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 108.47 (10) | C1—C6—H6 | 119.9 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 110.74 (12) | C12—C7—C8 | 120.0 (2) |
| O2—S1—C1 | 106.38 (11) | C12—C7—N1 | 119.82 (19) |
| N1—S1—C1 | 105.32 (10) | C8—C7—N1 | 120.19 (18) |
| C13—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C9—C8—C7 | 118.12 (19) |
| C7—N1—S1 | 123.33 (14) | C9—C8—C13 | 120.35 (19) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 118.3 | C7—C8—C13 | 121.44 (18) |
| S1—N1—H1 | 118.3 | C10—C9—C8 | 121.9 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.5 (2) | C10—C9—Cl3 | 118.17 (18) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 116.6 (2) | C8—C9—Cl3 | 119.94 (18) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 122.88 (19) | C11—C10—C9 | 118.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.2 (3) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.5 |
| C1—C2—Cl2 | 121.7 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.5 |
| C3—C2—Cl2 | 120.2 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.2 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.7 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 119.1 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 120.2 (3) | C11—C12—C7 | 119.8 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.4 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.1 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 | C7—C12—H12 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 | O4—C13—O3 | 123.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.0 (3) | O4—C13—C8 | 119.58 (19) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | O3—C13—C8 | 116.82 (18) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | ||
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | −178.47 (17) | S1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.3 (3) |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | −49.3 (2) | S1—N1—C7—C12 | 55.1 (3) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | 64.24 (19) | S1—N1—C7—C8 | −125.01 (19) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | 132.5 (2) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 3.9 (3) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | 1.4 (2) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | −175.94 (19) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | −113.6 (2) | C12—C7—C8—C13 | −172.5 (2) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | −49.0 (2) | N1—C7—C8—C13 | 7.6 (3) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 179.83 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −4.4 (3) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | 64.8 (2) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 172.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.0 (4) | C7—C8—C9—Cl3 | 173.60 (17) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.45 (19) | C13—C8—C9—Cl3 | −9.9 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl2 | −178.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.0 (4) |
| S1—C1—C2—Cl2 | 2.9 (3) | Cl3—C9—C10—C11 | −177.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.1 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 3.0 (4) |
| Cl2—C2—C3—C4 | 178.6 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −3.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | 178.77 (19) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.2 (4) |
| Cl2—C2—C3—Cl1 | −1.5 (3) | N1—C7—C12—C11 | 179.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (5) | C9—C8—C13—O4 | −56.9 (3) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | −179.4 (3) | C7—C8—C13—O4 | 119.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.4 (6) | C9—C8—C13—O3 | 124.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.5 (5) | C7—C8—C13—O3 | −58.9 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.2 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O3 | 0.86 | 2.55 | 2.940 (2) | 108 |
| C12—H12···O3i | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.425 (3) | 150 |
| O3—H3···O4ii | 0.82 | 1.85 | 2.666 (2) | 176 |
| N1—H1···O2iii | 0.86 | 2.30 | 3.128 (2) | 162 |
| C5—H5···O4iv | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.256 (4) | 135 |
| C10—H10···O1v | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.165 (3) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (v) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5312).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Arshad, M. N., Danish, M., Tahir, M. N., Aabideen, Z. U. & Asiri, A. M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M. N., Khan, I. U., Rafique, H. M., Asiri, A. M. & Shafiq, M. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M. N., Tahir, M. N., Khan, I. U., Siddiqui, W. A. & Shafiq, M. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem. 1, 189-191.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011574/hg5312sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011574/hg5312Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011574/hg5312Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report