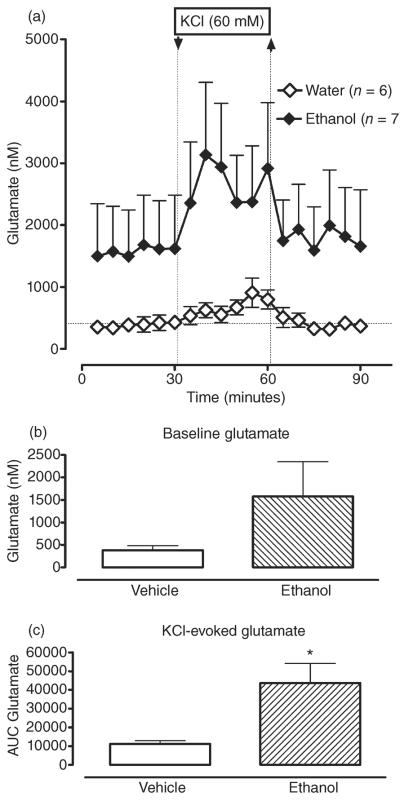
Figure 3.
Repeated intermittent administration of ethanol (3.4 g/kg, intragastrically via gavage, once daily × 6 days) increases dialysate glutamate levels in dorsal hippocampus (CA3). (a) Time course of dialysate glutamate levels in the CA3 area of hippocampus in water- (white circles) and ethanol-treated (black circles) animals before and after reversed dialysis of KCl (60 mM.; arrow and dotted line). Data are expressed as the means ± SEM. n = number of animals in each experimental group (6–7 animals per group). (b) Bar graphs of basal GABA levels in water- and ethanol-treated animals expressed as the means ± SEM. (c) Bar graphs of AUC values for the GABA response to KCl expressed as the means ± SEM. *Significant difference in KCl-induced glutamate responses between water- and ethanol-treated animals (P ≤ 0.05). AUC, area under the curve; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; SEM, standard error of the mean