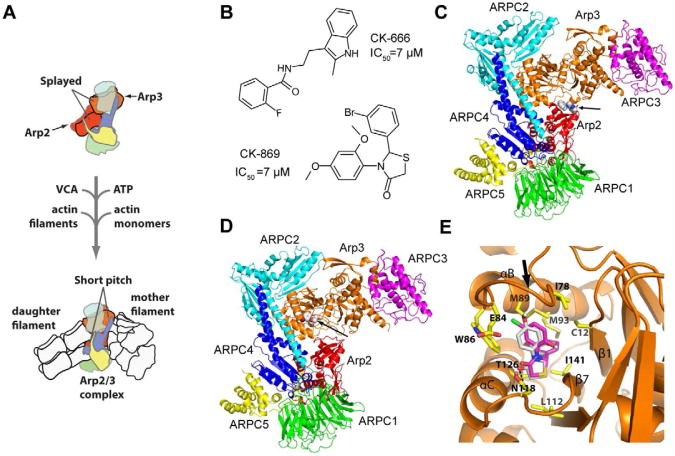
Fig. 1.
CK-666 and CK-869 bind to different sites on Arp2/3 complex. (A) Overview of branching nucleation reaction showing proposed conformational change of Arp2 and Arp3 into the activated short pitch conformation. (B) Structures of CK-666 and CK-869. Previously reported IC50 values are indicated (Nolen et al., 2009). (C) Overall binding mode of CK-666 from a previously reported 2.5 Å x-ray crystal structure of CK-666 bound to Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex (3UKR) (Baggett et al., 2012). CK-666 (marked with arrow) binds at the interface of Arp3 (orange) and Arp2 (red). The other subunits of the complex are ARPC1-5, and are colored green, cyan, magenta, blue and yellow, respectively. CK-666 binding does not change the position of the subunits compared to inhibitor-free structures, but appears to stabilize the splayed (inactive) conformation of the Arp2 and Arp3 subunits. (D) Overall binding mode of CK-869 from the 2.75 Å x-ray crystal structure reported here. CK-869 (marked with arrow) binds to a hydrophobic pocket in Arp3 (orange). Color scheme is identical to panel (C). (E) Close up of the binding pocket of CK-869. The binding site for CK-869 (grey) is identical to the site for CK-548 (magenta) and is exposed when the sensor loop (arrow) flips into an open conformation. See also Figure S1 and Table S1.