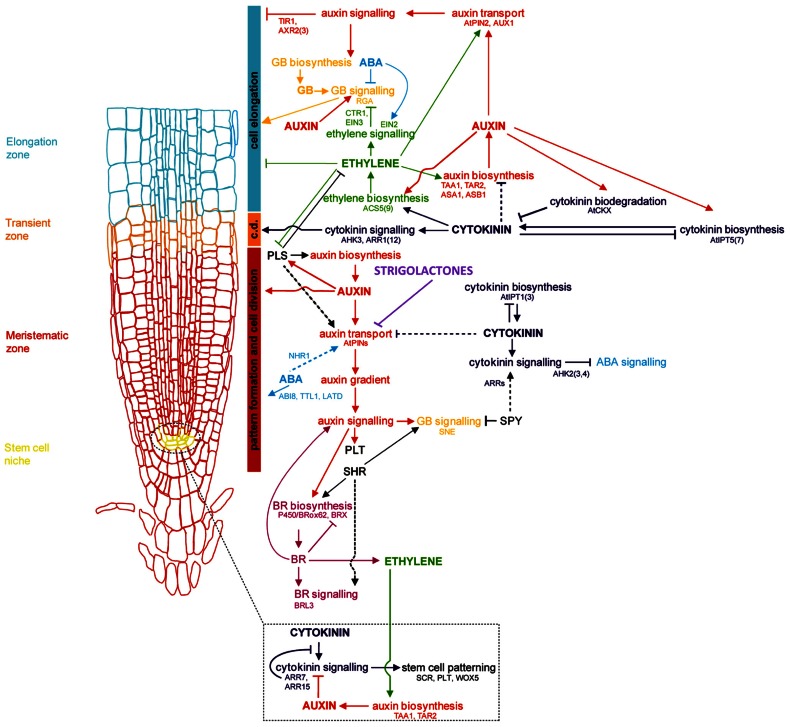
FIGURE 1.
Genetic and hormonal control of primary root development in Arabidopsis Model of the current understanding of hormone interaction and genetic regulation of primary root and general root apical meristem growth and development in Arabidopsis. Important genes involved in integrating signals from different hormone pathways are shown in black; hormone networks are color-coded; dashed lines represent unresolved or indirect relations. The fundamental role of auxin-mediated signaling in controlling all major aspects of root growth, from cell division, differentiation, and elongation, can be visualized, as well as the antagonistic regulation of auxin by cytokinins, and secondary regulation by other hormones, including ABA, ethylene, GA, brassinosteroids (BRs), and strigolactones. c.d. is “cell differentiation,” in reference to the transition zone where cell differentiation is initiated (modified from Benkova and Hejatko, 2009).