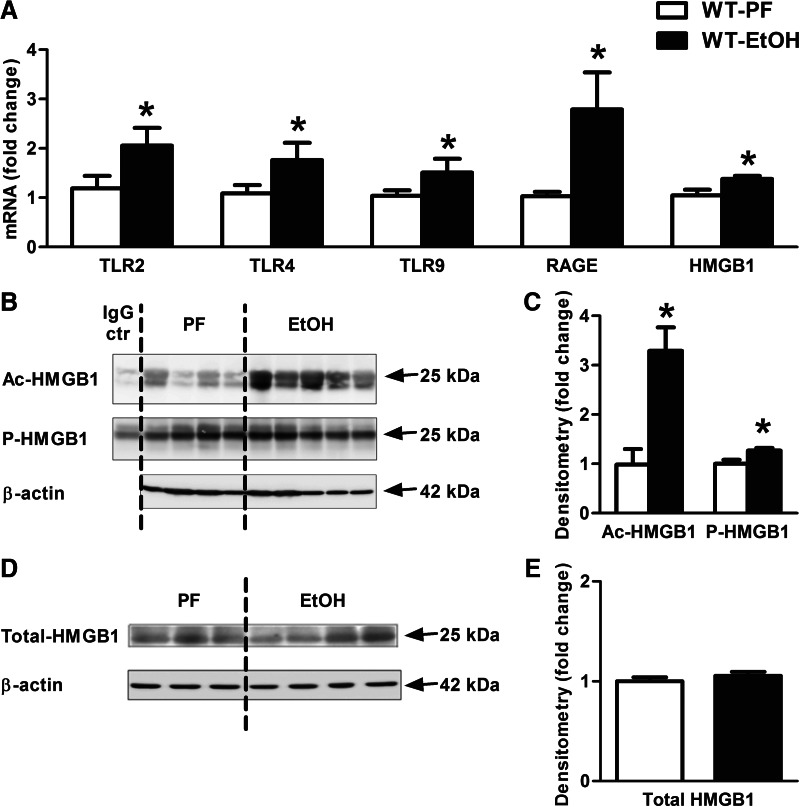
Figure 3. Active endogenous danger molecule, HMGB1, and its receptors are elevated in alcohol-fed mice in the cerebellum.
WT mice were fed with an EtOH (n=6) or a control (PF; n=8) diet for 5 weeks. TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, and RAGE receptors and HMGB1 (A) were assessed by real-time PCR from whole cerebellar RNA extracts, normalized to 18S. Acetyl (Ac)- and phospho (P)-HMGB1 of whole cerebellar lysates were analyzed by IP (B) and assessed further by densitometry, using β-actin Western blot for loading control on a separate gel (C). Cerebellar lysate of one representative ethanol-fed mouse was applied for IgG control (ctr), using the same amount of protein. Total HMGB1 of whole cerebellar lysates was analyzed by Western blot using β-actin as a loading control (D) and quantified further by densitometry (E). Bars represent mean ± sem (*P<0.05, relative to appropriate PF controls by the Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test).