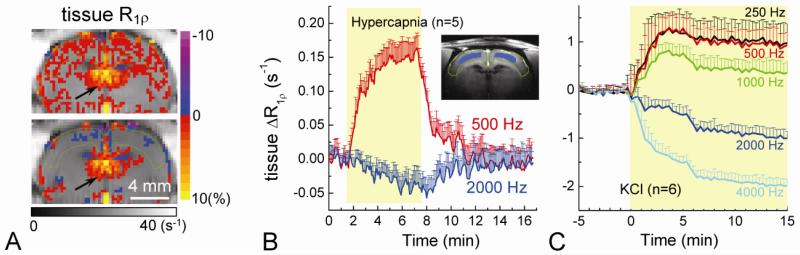
Fig. 6. Spin-locking frequency-dependent tissue R1ρ change during tissue acidosis.
Tissue R1ρ changes were measured during hypercapnia and global ischemia after 5 mg/kg MION injection. Tissue R1ρ change maps for ω1 = 500 Hz and 2000 Hz are shown for hypercapnic challenge in one rat (A). Green contour indicates the cortical area. Unlike visual stimulation, an increase in tissue R1ρ was observed for ω1 = 500 Hz. Note that the increases of R1ρ near the ventricle area are similar in the two maps and can be attributed to a change of CSF volume fraction (arrows). The averaged time course (n = 5 rats) of the tissue R1ρ response obtained the cortical ROI (Inset) shows a significant increase for 500 Hz whereas a small decrease for 2000 Hz (B). The averaged tissue R1ρ responses (n = 6 rats) for ω1 from 250 to 4000 Hz during KCl injection (C), which induces tissue acidosis, show spin-locking frequency-dependent changes. These are qualitatively similar to hypercapnia.