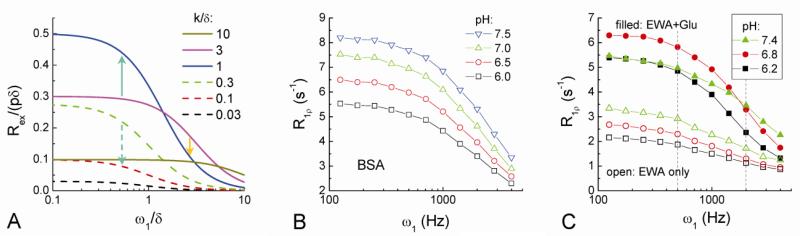
Fig. 7. Calculated Rex dispersion (A) and the measured R1ρ dispersion of pH-dependent phantoms (B-C).
Rex dispersion was calculated with Eq. [4] as a function of exchange rate k. Upward and downward arrows indicate changes in Rex when the exchange between labile protons and water is slow down due to pH decrease (see texts). The R1ρ dispersion of 8% bovine serum albumin (BSA) decreases with pH values (B). The R1ρ dispersion of 4% egg white albumin (EWA) only (open symbols) and 4% EWA with 30 mM of glutamate (filled symbols) were both measured for three pH values (C). Vertical dashed lines (C) indicate spin-locking frequencies of 500 and 2000 Hz used for in vivo studies. The addition of glutamate (Glu) changes the pH-dependence of R1ρ dispersion.