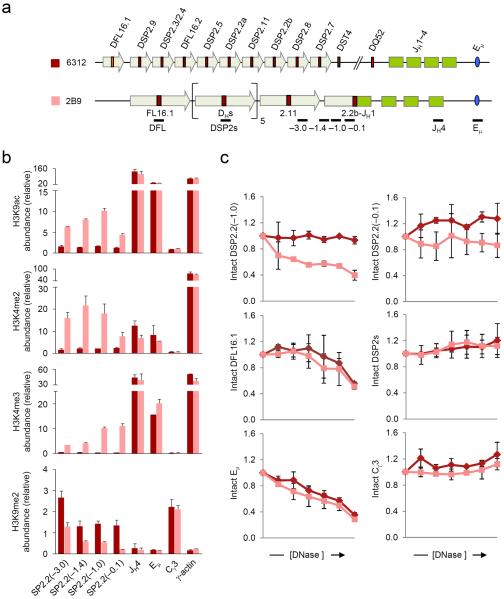
Figure 1. Chromatin accessibility at DSP2.2b-JH1 rearranged allele.
(a) Schematic of the germline Igh locus in 6312 cells and the DJH rearranged Igh locus in 6312-derivative 2B9 cells, which harbor a DSP2.2b-JH1 junction in one allele and a VH rearrangement in the other allele (not to scale). The positions of amplicons analyzed by real-time PCR are also shown. Block arrows represent DH-associated repeat sequences10,11. (b) ChIP assays were performed using antibodies for modified histones as indicated with chromatin obtained from 6312 (maroon bars) and 2B9 (pink bars) cells. The numbers within the parentheses indicate positions in kb 5′ of the DSP2.2b segment. All samples were assayed in duplicate by real-time PCR and relative abundance (y axis) for each amplicon in the immunoprecipitate was calculated as previously described11. γ-actin promoter and Cγ3 served as controls for active and inactive chromatin, respectively. Data show the average of 2 independent ChIP experiments and error bars indicate standard deviation. (c) DNase I sensitivity analyses of the DSP2.2b-JH1 allele (pink lines) compared to the germline Igh allele (maroon lines). 2×106 nuclei from 6312 and 2B9 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of DNase I (x axis, 0 to 2 units of DNase I) followed by purification of the genomic DNA. All samples were assayed in duplicate by quantitative real-time PCR and the proportion of intact DNA (y axis) at each DNase I concentration was determined for the indicated amplicon as previously described18. Eμ corresponds to the known DNase I hypersensitive site in the JH-Cμ intron, while Cγ3 is DNase I insensitive. Data show the average of 2 independent DNase I sensitivity experiments and error bars indicate standard deviation.