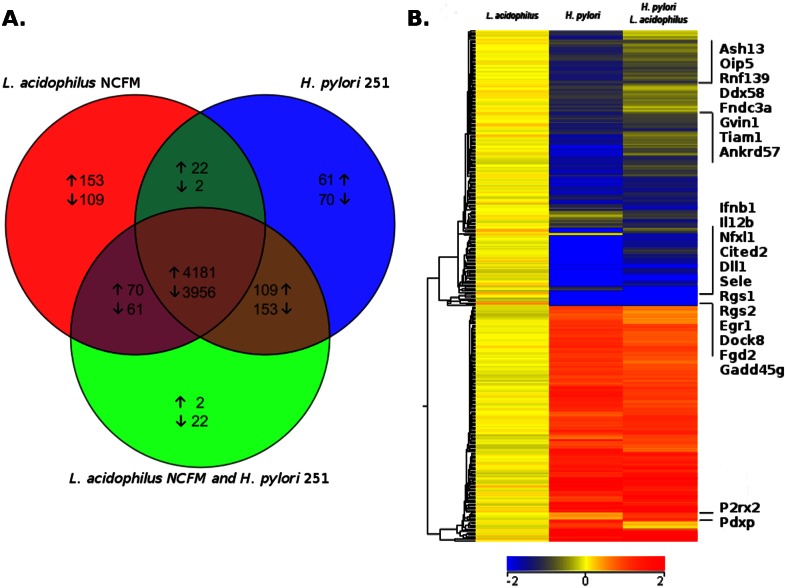
FIG 1 .
H. pylori modulates the stimulatory profile induced by L. acidophilus in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages. Murine BMDMs from three individual mice were stimulated for 5 h with either L. acidophilus NCFM or H. pylori 251 or prestimulated with L. acidophilus NCFM for 1 h prior to the addition of Helicobacter pylori 251. (A) Venn diagram illustrating pairwise overlap of differentially expressed genes (P < 0.01; fold change greater than ±2) by one-way ANOVA with Benjamini-Hochberg multiple testing correction. (B) Heat map of differentially expressed genes (P < 0.01, fold change greater than ±1.5) expressed at a lower or higher rate than with L. acidophilus treatment. Blue designates genes expressed at a lower level than with L. acidophilus alone, while red indicates greater expression. Data were classified using hierarchical clustering by genes with Euclidean distances and centroid linkage rules.