Abstract
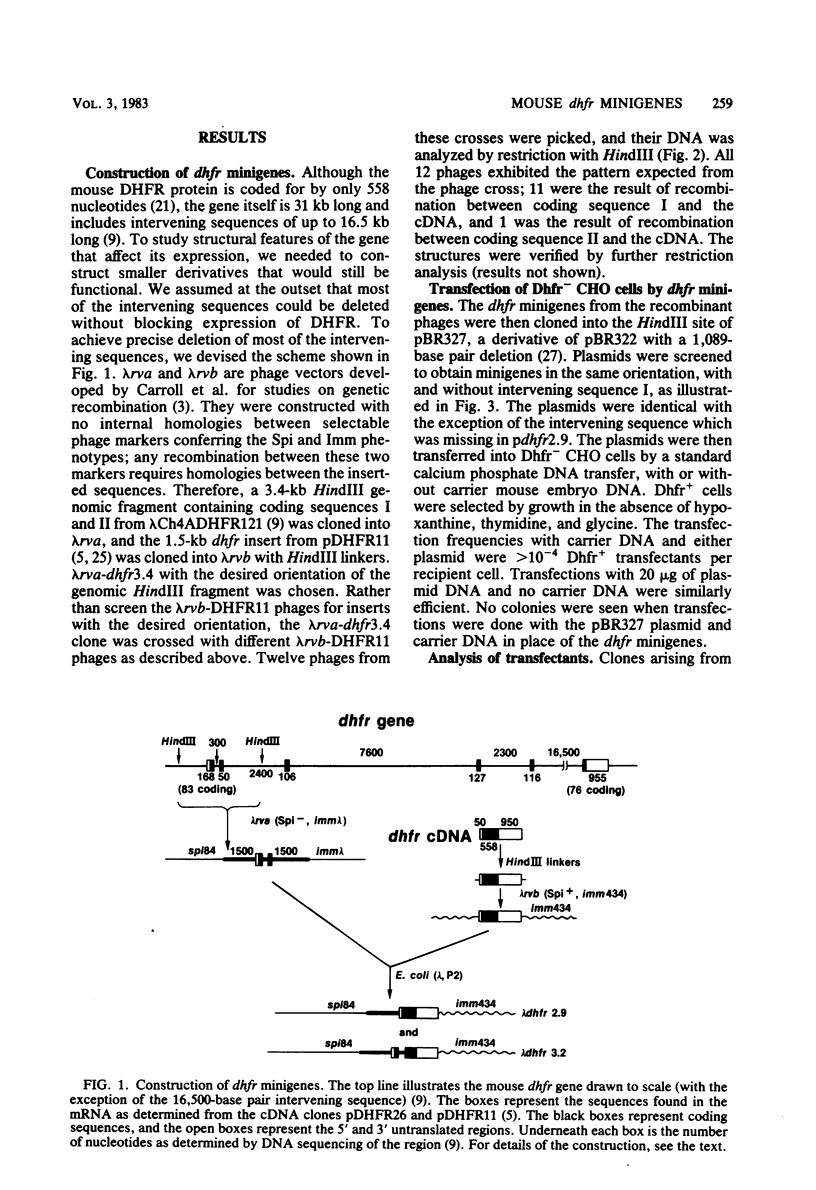
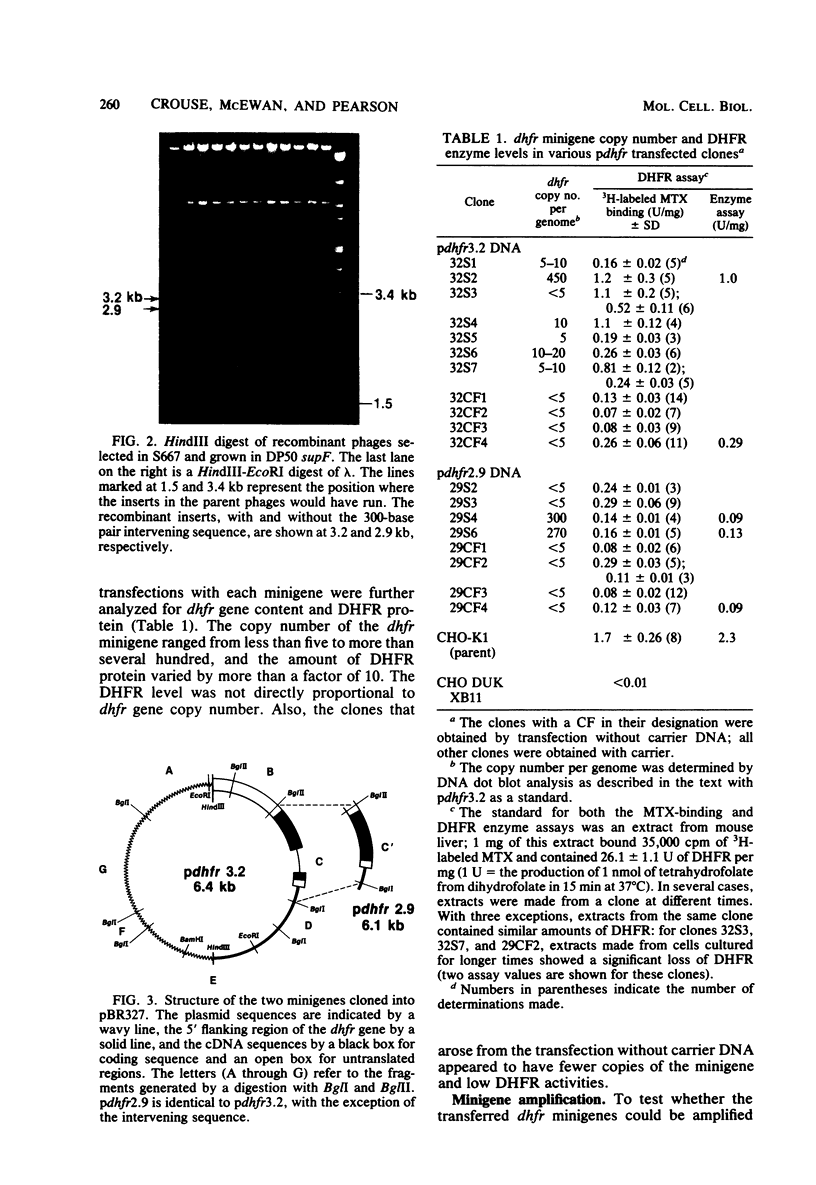
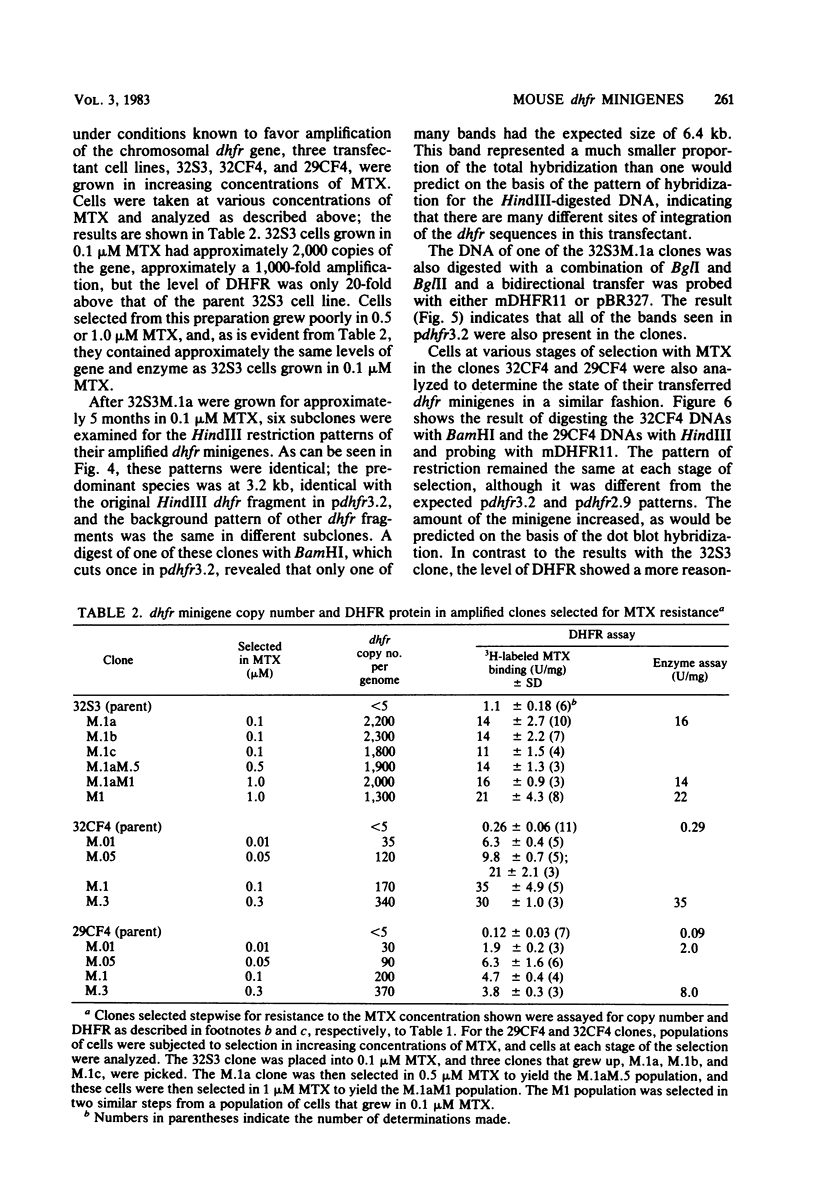
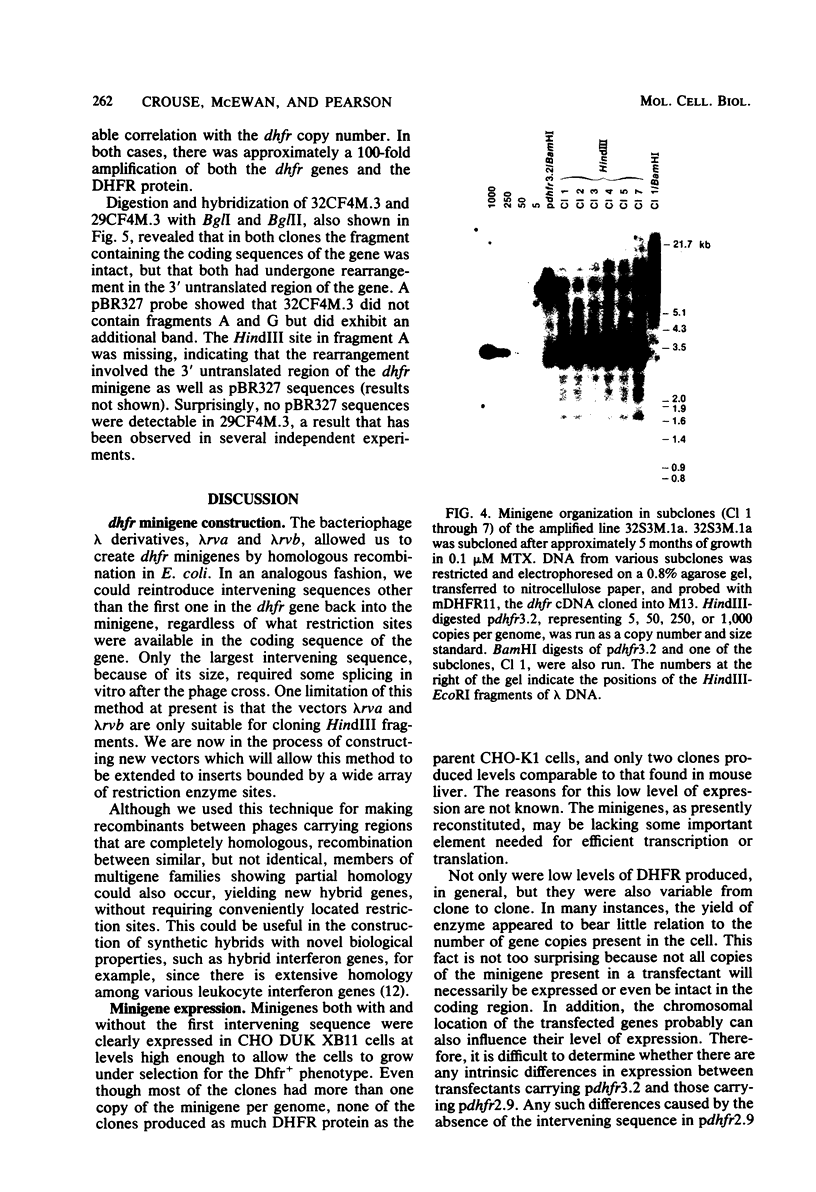
We constructed mouse dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) minigenes (dhfr) that had 1.5 kilobases of 5' flanking sequences and contained either none or only one of the intervening sequences that are normally present in the coding region. They were greater than or equal to 3.2 kilobase long, about one-tenth the size of the corresponding chromosomal gene. Both of these minigenes complemented the DHFR deficiency in Chinese hamster ovary dhfr-1-cells at a high frequency after DNA-mediated gene transfer. The level of DHFR enzyme in various transfected clones varied over a 10-fold range but never was as high as in wild-type Chinese hamster ovary cells. In addition, the level of DHFR in primary transfectants did not vary directly with the copy number of the minigene, which ranged from fewer than five to several hundred per genome. The minigenes could be amplified to a level of over 2,000 copies per genome upon selection in methotrexate, a specific inhibitor of DHFR. In one case, the amplified minigenes were present in a tandem array; in two other cases, a rearranged minigene plasmid and its flanking chromosomal DNA sequence were amplified. Thus, the mouse dhfr minigenes could be transcribed, expressed, and amplified in Chinese hamster ovary cells, although the efficiency of expression was generally low. The key step in the construction of these minigenes was the generation in vivo of lambda phage recombinants by overlapping regions of homology between genomic and cDNA clones. The techniques used here for dhfr should be generally applicable to any gene, however large, and could be used to generate novel genes from members of multigene families.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Warren R., Sarthy A., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein--thymidine kinase fusion plasmids injected into mouse eggs. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):39–42. doi: 10.1038/296039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Ajioka R. S., Georgopoulos C. Bacteriophage lambda cloning vehicles for studies of genetic recombination. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarone C. F., Bolognesi C., Santi L. Improved microfluorometric DNA determination in biological material using 33258 Hoechst. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):188–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
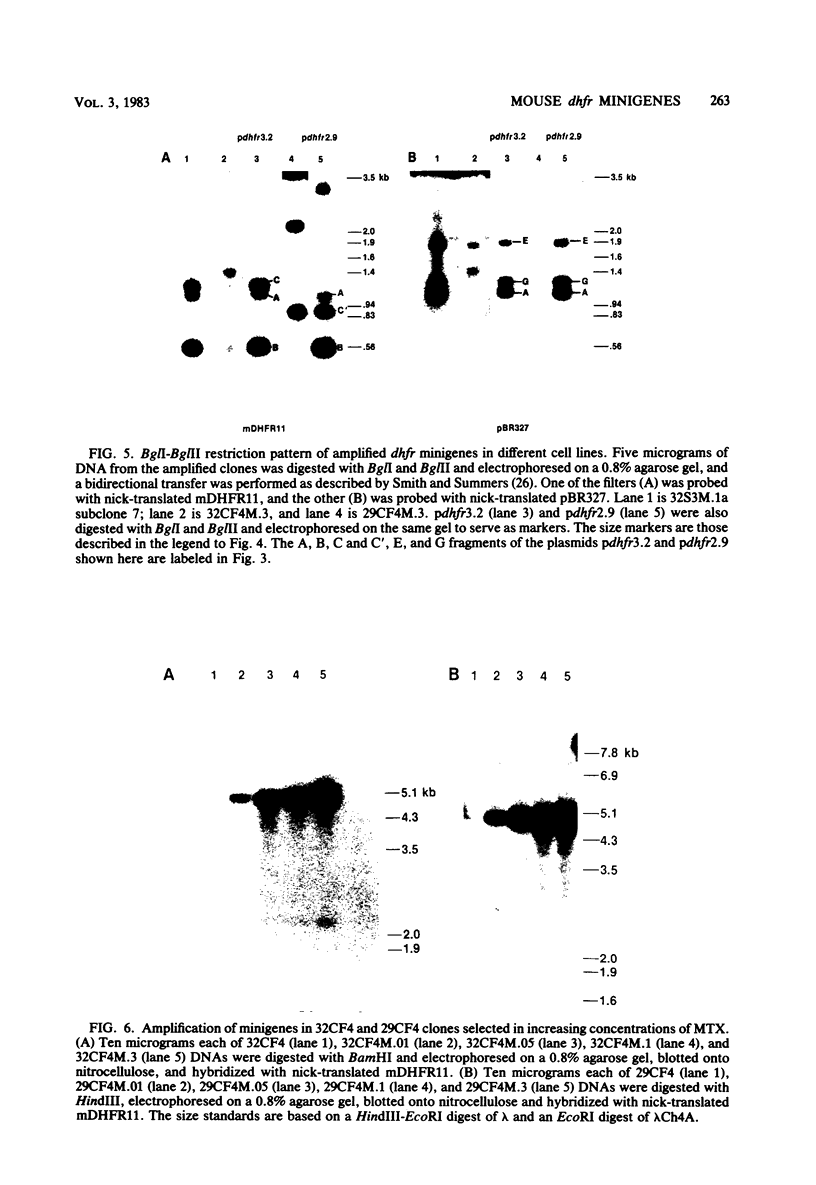
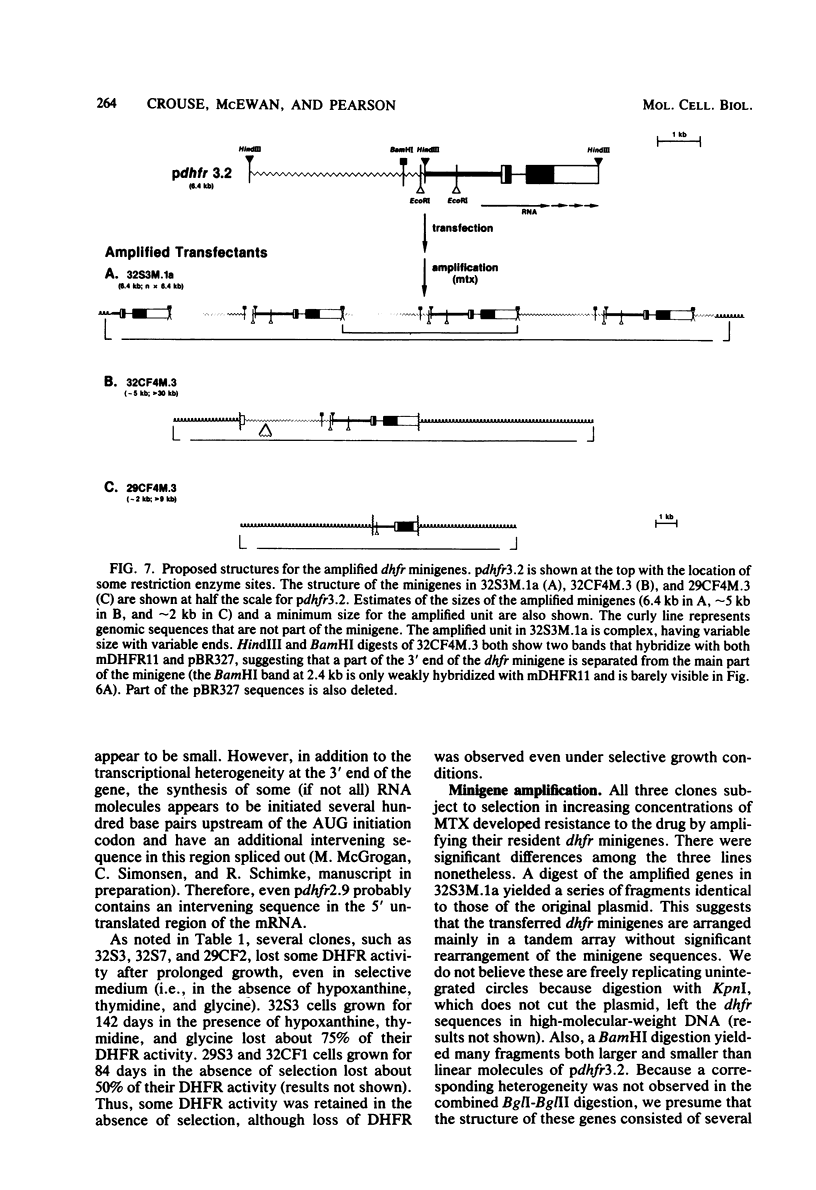
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Mantei N., Weissmann C. DNA sequences preceding the rabbit beta-globin gene are required for formation in mouse L cells of beta-globin RNA with the correct 5' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Madden M. J., Schiop-Stanley P., Vande Woude G. F. Cloning of herpes simplex type 1 DNA fragments in a bacteriophage lambda vector. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):541–544. doi: 10.1126/science.216076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber D. A., Beverley S. M., Kiely M. L., Schimke R. T. Properties of an altered dihydrofolate reductase encoded by amplified genes in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9501–9510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman R., McGready R., Van der Weyden M. B. A rapid radiometric assay for dihydrofolate reductase. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):460–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90696-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung N., Roginski R. S., Henthorn P., Smithies O., Kucherlapati R., Skoultchi A. I. Introduction and expression of a fetal human globin gene in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):401–411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. T. Hormonal inducibility of rat alpha 2u globulin genes in transfected mouse cells. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):629–631. doi: 10.1038/291629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Boll W., Weissmann C. Rabbit beta-globin mRNA production in mouse L cells transformed with cloned rabbit beta-globin chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):40–46. doi: 10.1038/281040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Inducer-responsive expression of the cloned human interferon beta 1 gene introduced into cultured mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):967–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G., Dieckmann B., Lee F. Co-expression and amplification of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA and the Escherichia coli XGPRT gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):165–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Kaufman R. J., Alt F. W., Kellems R. F. Gene amplification and drug resistance in cultured murine cells. Science. 1978 Dec 8;202(4372):1051–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.715457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Perucho M., Kurtz D., Dana S., Pellicer A., Axel R., Silverstein S. Transformation of mammalian cells with an amplifiable dominant-acting gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3567–3570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Clements J. B., Boll W., Mantei N., Lonsdale D., Weissmann C. Hybrid plasmids containing an active thymidine kinase gene of Herpes simplex virus 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):859–877. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold B., Wigler M., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Introduction and expression of a rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5684–5688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







