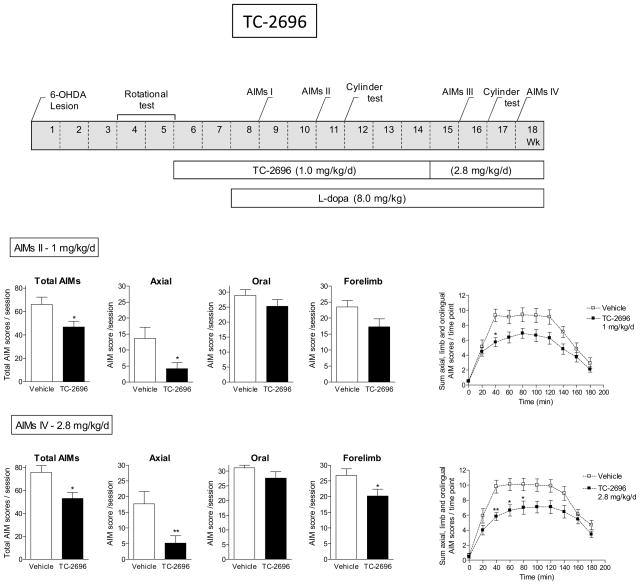
Fig. 4.
Decline in L-dopa-induced AIMs with TC-2696. The treatment regimen is depicted in the upper panel. All rats were unilaterally lesioned with 6-OHDA as described in Methods. They were then pretreated with TC-2696 (1.0 mg/kg/d) for 2 wk via minipump and subsequently injected with L-dopa plus benserazide (8.0 mg/kg plus 15 mg/kg sc). After several wk at 1.0 mg/kg/d TC-2696, the initial minipump was replaced with one releasing 2.8 mg/kg/d. The rats were assessed for axial, oral and forelimb AIMs as indicated in the timeline, with the total AIMs representing the sum of these three components. The daily time course of the total L-dopa-induced AIMs is depicted in the graphs at the right. Values are the mean ± S.E.M. of 9–10 rats per group. Significance of difference from vehicle: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.