Figure 2.
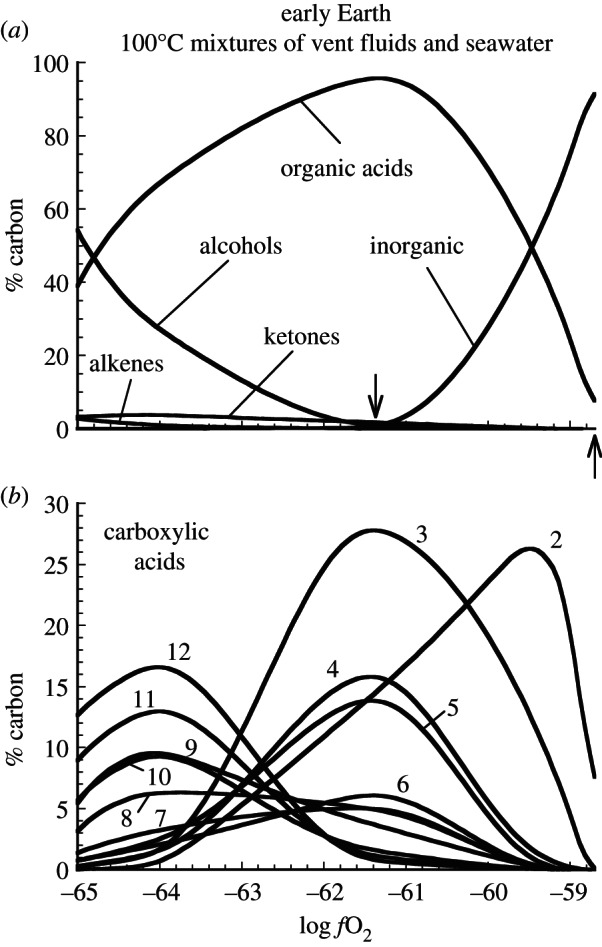
Calculated consequences for carbon speciation of attaining metastable equilibrium states at 100°C in mixtures of seawater with submarine hydrothermal vent fluids of variable initial redox state on the early Earth (derived from results presented in Shock & Schulte [46]). In (a), the upward pointing arrow indicates conditions in a 100°C mixture of seawater and 350°C vent fluid initially at PPM, and the downward pointing arrow locates conditions prevailing in a 100°C mixture of seawater and 350°C vent fluid initially at FMQ. ‘Inorganic’ refers to the sum of dissolved CO2, carbonate, bicarbonate and their complexes. In (b), numbers indicate carbon-chain length of n-carboxylic acids (2 = acetic acid, etc.).
