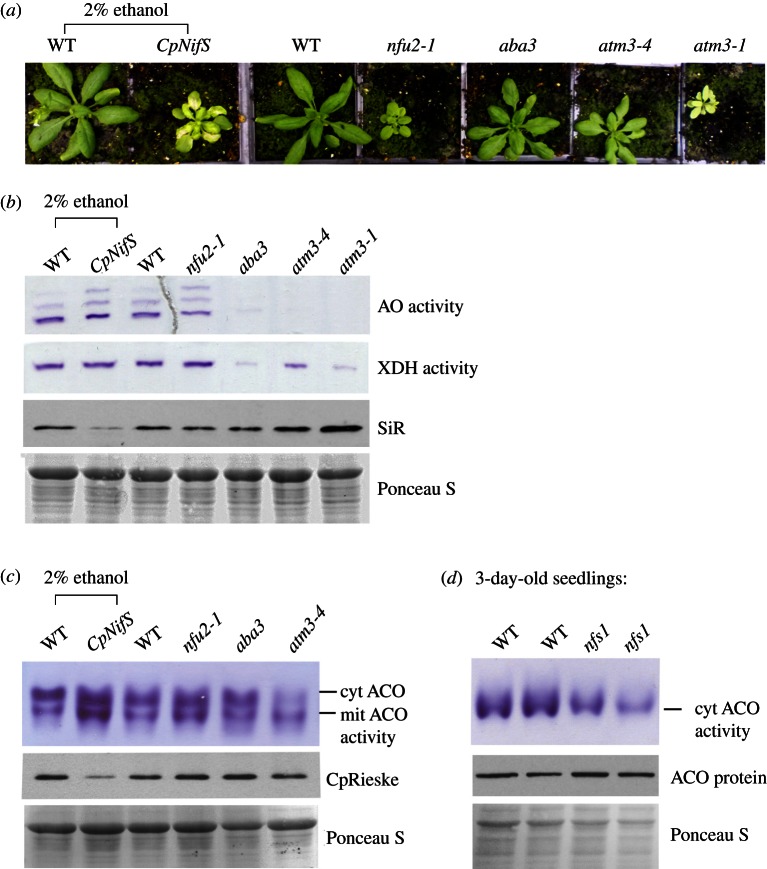
Figure 1.
Fe–S enzyme activities in Arabidopsis mutants in Fe–S cluster and Moco assembly genes. (a) Growth phenotypes of wild-type (WT) and mutants in the following genes: the plastid cysteine desulfurase CpNifS, downregulated by expression of an ethanol-inducible RNAi; the plastid Fe–S cluster scaffold NFU2; the Moco sulfurase ABA3 (sir3-3 allele); the mitochondrial ABC transporter ATM3, of which a weak allele (atm3-4) and strong allele (atm3-1) are shown. (b) Leaf extracts from 4-week-old plants of WT and the indicated Arabidopsis mutants were separated by native gel electrophoresis and stained for activity of aldehyde oxidases (AO) and xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH). Protein samples of the same extracts (20 μg) were separated by SDS–PAGE, blotted and labelled with antibodies against sulfite reductase (SiR). The blots were stained with Ponceau S to confirm equal protein loading. (c) Leaf extracts from four-week-old WT and mutant plants were separated on native starch-poly acrylamide gels and stained for aconitase activities (ACO) localized in the cytosol (cyt) or mitochondria (mit). Aliquots of 20 μg protein were also separated on denaturing gels, blotted and immuno-labelled for the Rieske Fe–S subunit of cytochrome b6f complex (CpRieske). Ponceau S staining confirmed equal protein loading. (d) Total extracts of 3-day-old seedlings from WT and nfs1 (a mutant in the mitochondrial cysteine desulfurase NFS1) were separated by native gel electrophoresis and stained for aconitase activity. At this developmental stage, only one dominant, cytosolic aconitase isoform is expressed; see the electronic supplementary material, figure S1. Protein of the same extracts (20 μg) were separated by SDS–PAGE, blotted and labelled with antibodies against aconitase, after staining with Ponceau S to confirm equal protein loading.