Fig. 1. Gene fine mapping and screening in family Z002 and the other DFNA4 families.
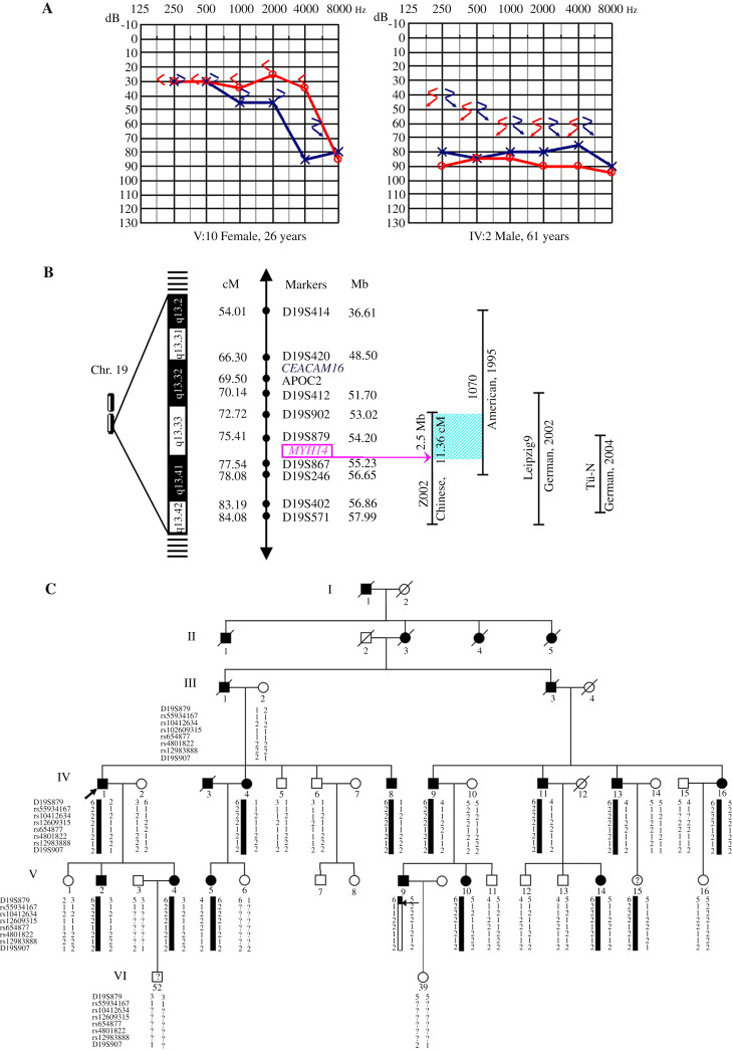
A: typical pure-tone audiograms of both ears from two affected subjects (V:10 and IV:2) in family Z002. ‘○’ connected by lines, right-ear air conduction; ‘×’ connected by lines, left-ear air conduction; ‘<’, right-ear bone conduction; ‘>’, left-ear bone conduction; ‘↙’ and ‘↘’, no response at maximum bone conduction output. B: schematic genetic and physical map of the DFNA4 locus on chromosome 19q13.2-q13.4 in families Z002, 1070, Leipzig9, and Tü-N. The shadowed area represents a 2.5-Mb region from marker D19S902 to the MYH14 gene shared by families Z002 and 1070. The genetic distances of microsatellite markers were obtained from the Marshfield genetic maps, and the physical distances of the markers were obtained from the NCBI database. cM, centimorgan; Mb, megabase. C: SNP haplotype analysis in family Z002. The analysis indicates a recombination (denoted by the horizontal arrow) between D19S879 and rs55934167 in affected subject V:9. The recombination allows exclusion of MYH14 from the candidate region of family Z002 and refines the region to ~2.5 Mb.
