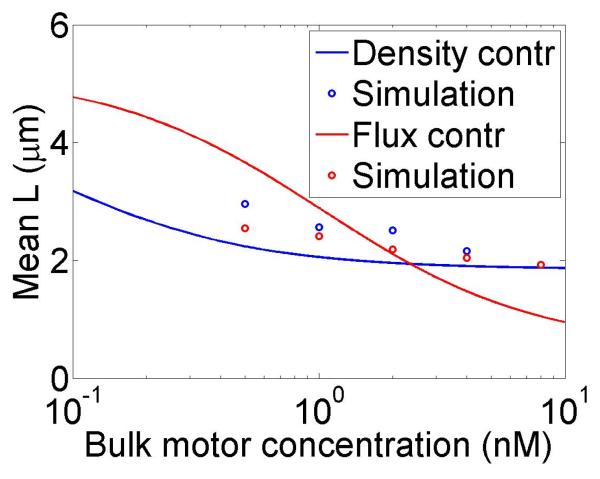
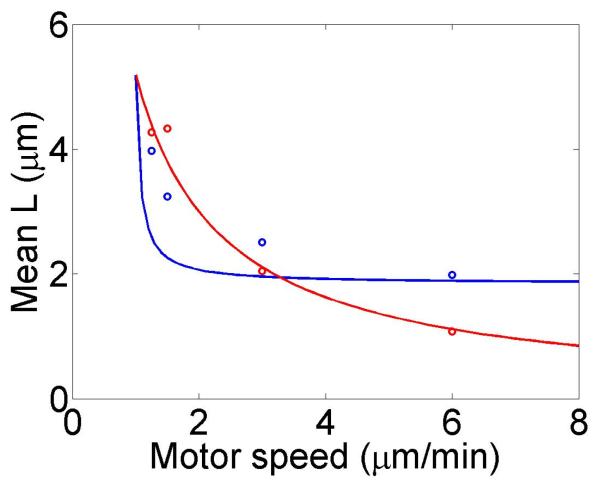
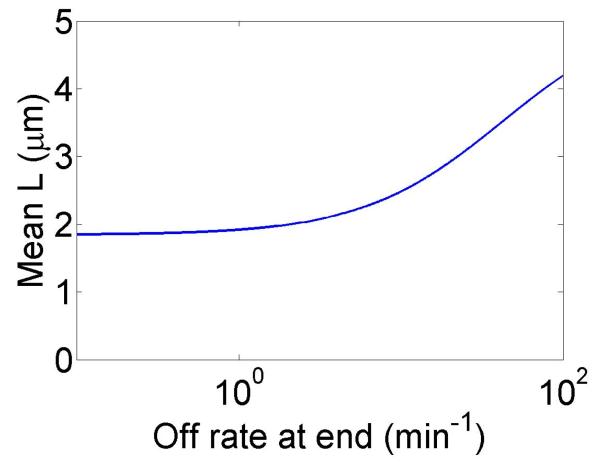
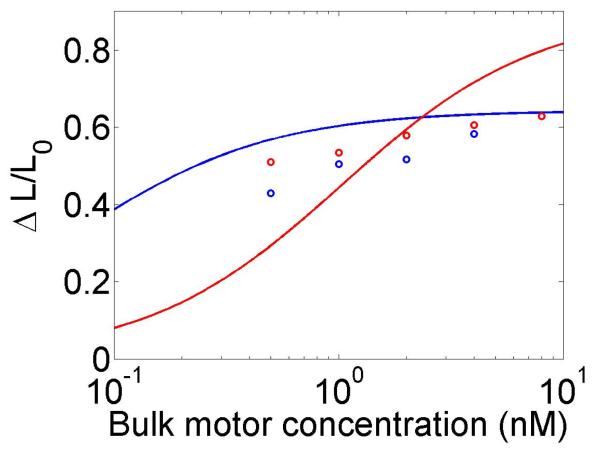
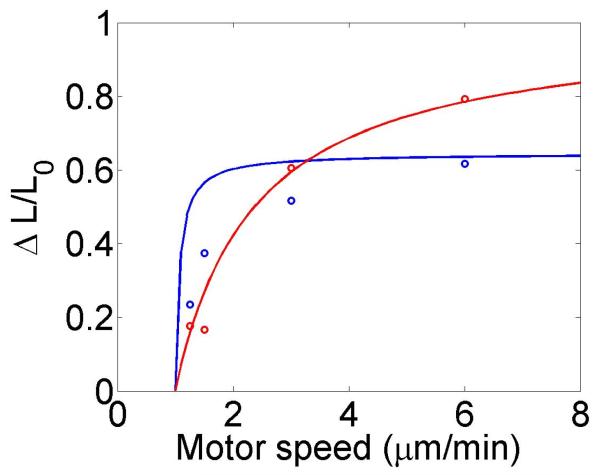
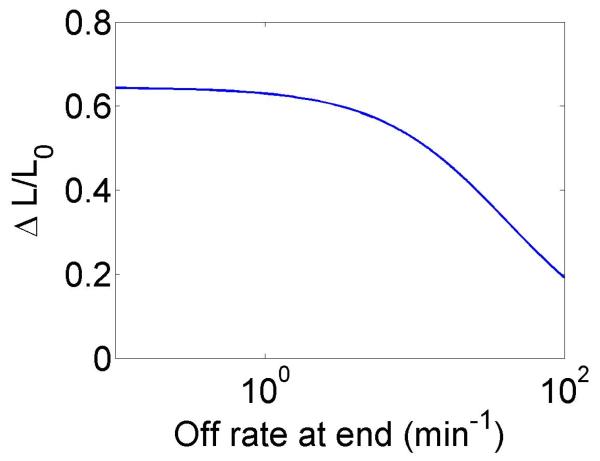
Figure 4.
Mean filament length and changes in filament length as a function of motor parameters. Left, variation as a function of bulk motor concentration. Center, variation as a function of motor speed. Right, variation as a function of in the density-controlled model. This figure uses the same parameters as figure 3 except where noted in varying the bulk motor concentration and motor speed: v = 3 μm min−1, u = 1 μm min−1, w = 7 μm min−1, minimum catastrophe frequency fc = 0.2 min−1, rescue frequency fr = 0.05 min−1, a = 8 nm, and ρmax = 125 μm−1. For the density-controlled model the parameters are kon = 1 nM−1 μm−1 min−1, koff = 0.25 min−1, min−1, bulk motor concentration c = 2 nM, and α = 0.35 min−1. The simulation of the density-controlled model has the same parameters except min−1 and α = 0.38 min−1. For the flux-controlled mean-field model the parameters are the same as for the density-controlled mean-field model except kon = 3 nM−1μm−1 min−1 and α = 7 × 10−3. The simulation of the flux-controlled model has the same parameters as the corresponding mean-field theory except kon = 1.5 nM−1μm−1 min−1 and α = 2 × 10−3.