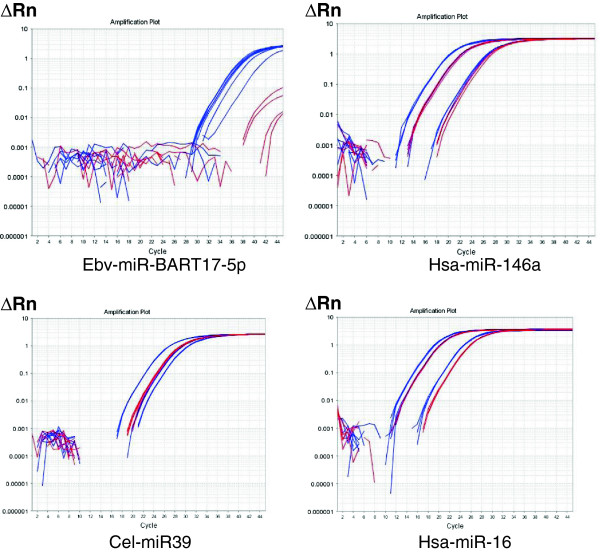
Figure 1.
Specific amplification of miR-BART17 in plasma RNAs from NPC patients (pilot study). Concentrations of miR-BART17, miR-146a, miR-16 and cel-miR-39 microRNAs were assessed by qRT-PCR in plasma RNAs from 3 NPC patients (8, 16, 17; blue) and 2 controls (patients C1, C2 bearing non-NPC Head and Neck carcinomas; red). ΔRn stands for the magnitude of the fluorescent signal generated during the PCR at each time point (with background correction). Hsa-miR-16 and hsa-miR-146a are two cellular microRNAs known to be abundant in most human plasma samples. Cel-miR-39 is a Caenorhabditis Elegans microRNA without homology to mammalian microRNAs. A constant amount of a synthetic cel-miR-39 microRNA was added to each plasma sample at an early stage of the RNA extraction procedure, providing an exogenous control in order to detect RNA extraction bias. Amplification curves for cel-miR-39 are homogeneous in all 5 samples confirming the quality of the RNA extraction procedures. In contrast, the amplification curves are heterogeneous for hsa-miR-16 and has-miR-146 but without separation of samples from NPC patients and from control donors. On the contrary, marked amplifications of miR-BART17 are only seen for samples from NPC patients.