Figure 1.
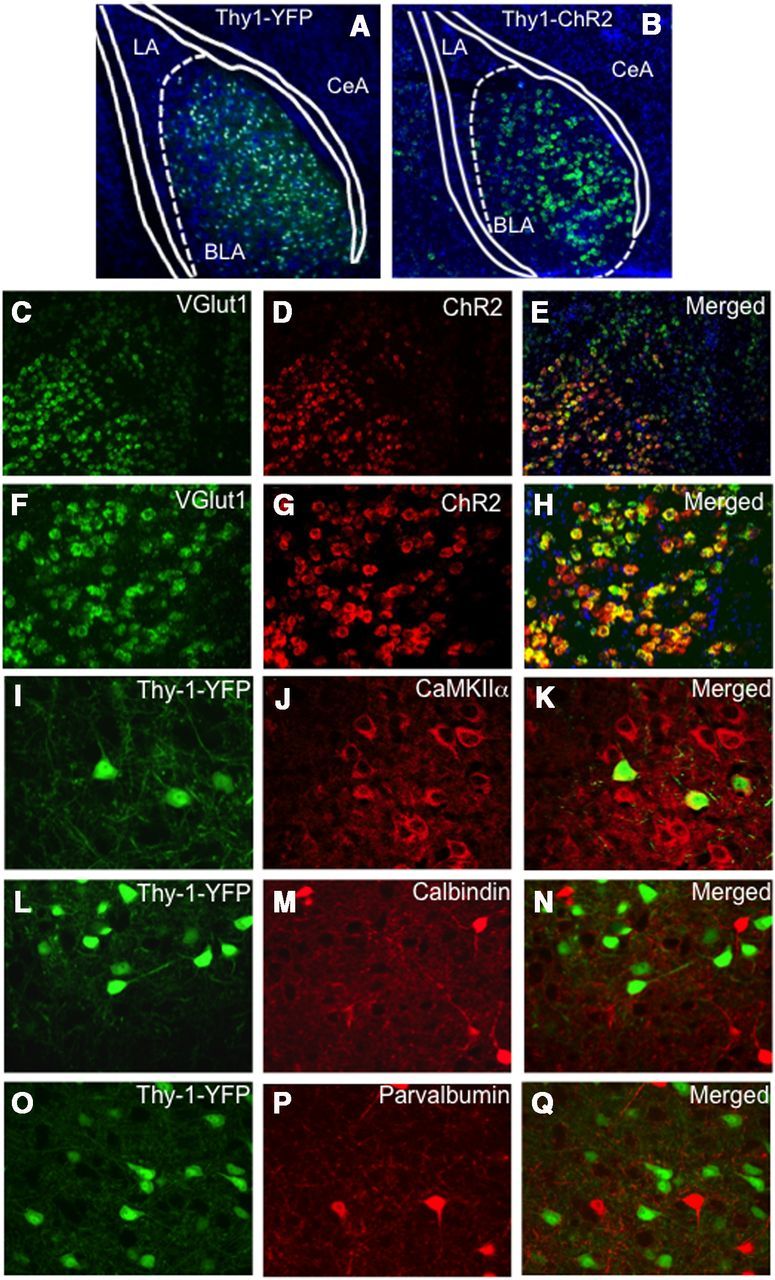
Molecular characterization of Thy1-expressing pyramidal neurons within basolateral amygdala transgene expression driven by the Thy1 promoter in two lines of mice (Thy1-YFP, Thy1-ChR2-EYFP). Extremely similar expression patterns of the two transgenes driven by the Thy1 promoter are observed in the BLA between the two lines. Although the expression pattern is the same, more cells appear labeled in A because of the thickness of the section (45 μm in A vs 16 μm in B). A, A coronal section of a Thy1-YFP mouse, double-labeled with DAPI (blue) staining all cells and YFP labeling the Thy1 subpopulation, in which the Thy1-YFP pyramidal neurons are only located in the BLA, and not the LA or CeA regions. B, A coronal section of a Thy1-ChR2-EYFP mouse identifying ChR2 transgene expression (green) using fluorescent in situ hybridization in which the Thy1-ChR2 neurons are only located in the BLA, and not the LA or CeA regions. Dual in situ hybridization for ChR2 and Vglut1 demonstrating that ChR2 neurons in the BLA are glutamatergic. C–E, Coronal sections (10×) of a Thy1-ChR2-EYFP mouse labeled with VGlut1 mRNA (green, C), ChR2 mRNA (red, D), and merged (E). F–H, Coronal sections (20×) of a Thy1-ChR2-EYFP mouse labeled with VGlut1 mRNA (green, F), ChR2 mRNA (red, G), and merged (H). All Vglut1 neurons do not express ChR2; however, virtually all ChR2 neurons express Vglut1 within the BLA. I–Q, Dual immunocytochemistry characterization of the Thy1-EYFP neuronal population in the Thy1-EYFP mouse line (green) and its colocalization with a subset of CaMKIIα neurons (I–K), but lack of colocalization with the inhibitory calbindin (L–N) or parvalbumin (O–Q) populations.
