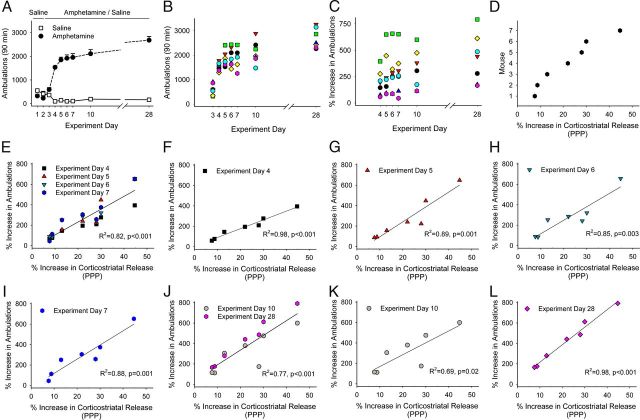
Figure 7.
PPP is proportional to the magnitude to locomotor sensitization. A, Locomotor ambulations in mice treated with either saline or amphetamine. B, Locomotor ambulations of individual mice after each amphetamine challenge from experiments shown in A. C, Percent increase in locomotor ambulations for individual mice shown in B, when normalized to ambulations after their first exposure to amphetamine (experiment day 3). D, Percent increase in corticostriatal release (PPP) as measured in slices from mice in A after killing on WD 50. E, Percent increase in ambulations of individual mice after amphetamine in vivo on experiment days 4–7 compared with PPP. F–I, PPP compared with the percent increase in ambulations on experiment days 4 (F), 5 (G), 6 (H), and 7 (I). J, Percent increase in ambulations after an amphetamine challenge in vivo on experiment days 10 and 28 compared with PPP. K, L, PPP compared with the percent increase in ambulations on experiment days 10 (K) and 28 (L).