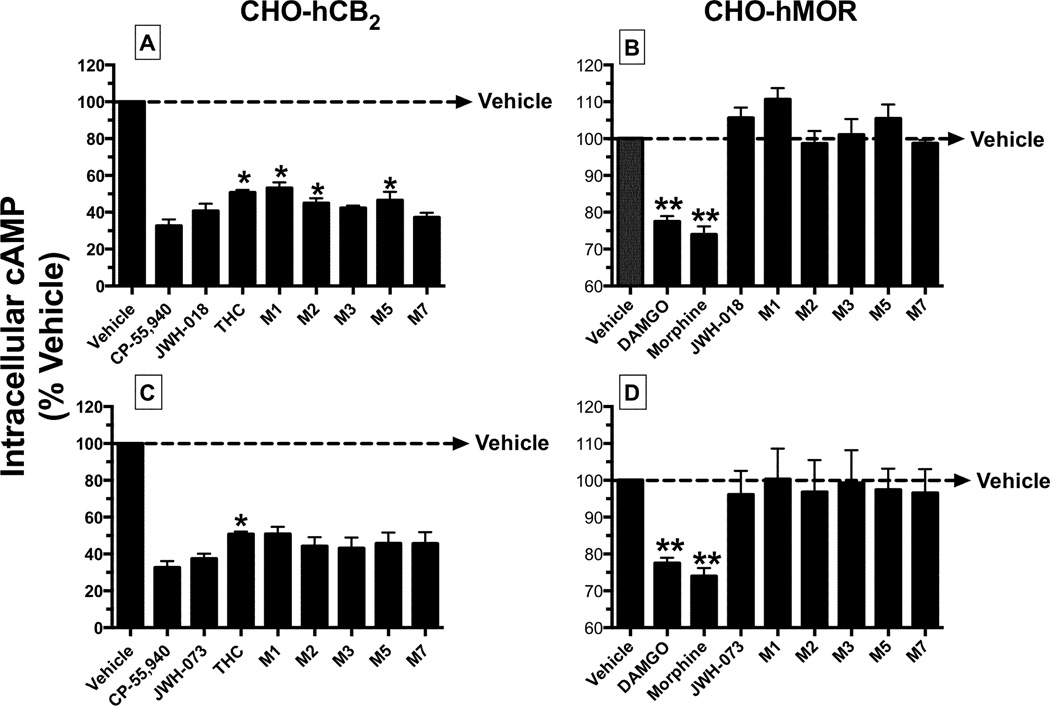
Figure 5. Monohydroxylated metabolites of JWH-018 and JWH-073 inhibit forskolin-stimulated adenylyl cyclase (AC)-activity via CB2Rs in intact cells.
A measure of maximal efficacy (EMAX) for CB2R-mediated inhibition of forskolin-stimulated AC-activity produced by JWH-018 [A] and [B], JWH-073 [C] and [D] and respective metabolites, was obtained by evaluating the level of intracellular cAMP levels in response to vehicle or a receptor saturating concentration (10 µM) of each test compound in intact CHO-hCB2 [A] and [C] or CHO-hMOR [B] and [D] cells. AC-inhibition produced by the MOR agonists DAMGO (10 µM) and morphine (10 µM) was evaluated as positive controls in CHO-hMOR cells. The mean ± SEM of AC-inhibition produced by test compounds is presented. EMAX values (mean ± SEM) are provided in Table 2.
*Significantly different from percent of AC-inhibition produced by CP-55,940 (P<0.05; ANOVA + Dunnett’s post-hoc comparison).
**Significantly different from basal cAMP levels (P<0.05; One sample t-test).