Fig. 2.
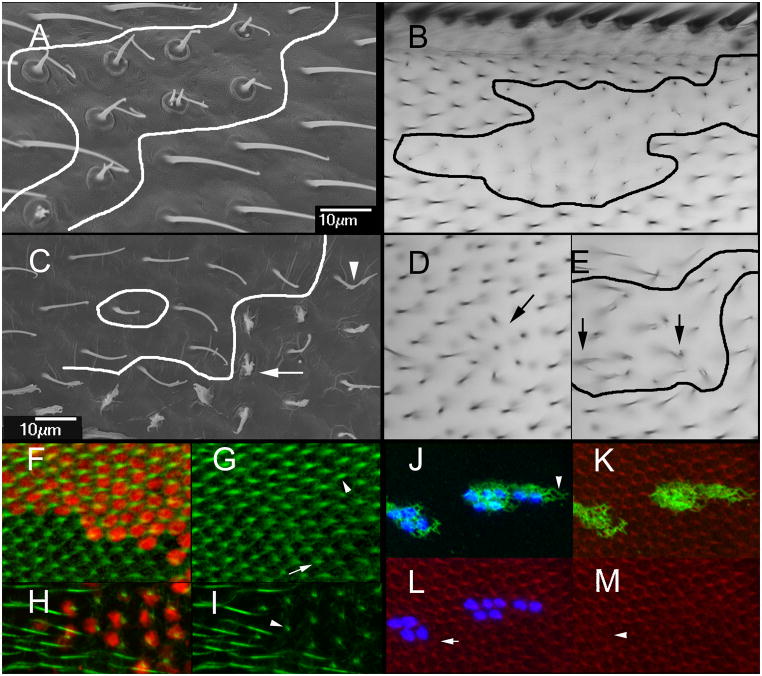
Cell autonomy of dyl. (A) An SEM of a dyl kd flip out clone. The putative clone boundary is outlined. Note the strong dyl phenotype of the putative clone cells juxtaposed to wild type hairs. (B). A light micrograph showing of of a dyl kd flip out clone. Once again note the wild type cells that are juxtaposed next to cells that show a strong dyl mutant phenotype. (C). An SEM of a dyl oe flip out clone. Note some cells show a very strong phenotype (arrow), some a weak phenotype (arrowhead) and others appear wild type. (D) A bright field micrograph of a small dyl oe clone. A small group of hairs appear to point inward (arrow). (E) A bright field micrograph of a larger dyl oe clone. The putative clone is outlined. As was observed in the SEM such clones contain cells that display a range of phenotypes. The arrows point to abnormal hairs. (F) A dyl kd flip out clone in a 33 hr pupal wing marked by the expression of LacZ (red). F-actin (green) shows the growing hairs. (G) The same wing as in F but with only the green (F-actin) channel. Note the clone hairs (arrowhead) are of wild type morphology at this stage and appear longer on average than the wild type neighbors (arrow). (H) A dyl kd flip out clone in a 46 hr pupal wing marked by the expression of LacZ (red). F-actin (green) shows the growing hairs. (I) The same wing as in H but with only the green channel shown. The phenotype of the dyl hairs is dramatic while neighboring wild type hairs show no phenotype. At this late stage F-actin staining is less vigorous and consistent from hair to hair than in younger wings particularly when combined with antibody staining. (J) A flip out dyl oe clone marked by the expression of LacZ (blue). Note the accumulation of Dyl is fibrous and extends beyond the clone cells (arrowhead). Note that the endogenous Dyl found in hairs is not visible at this level of exposure. (K). The same cells as in J with F-actin staining shown. (L). The same cells as in J with actin and LacZ shown. Note that some wild type cells show abnormal hair F-actin (arrow). (M). The same cells showing only F-actin staining. NBote that some kd cells also display abnormal hair F-actin (arrowhead).