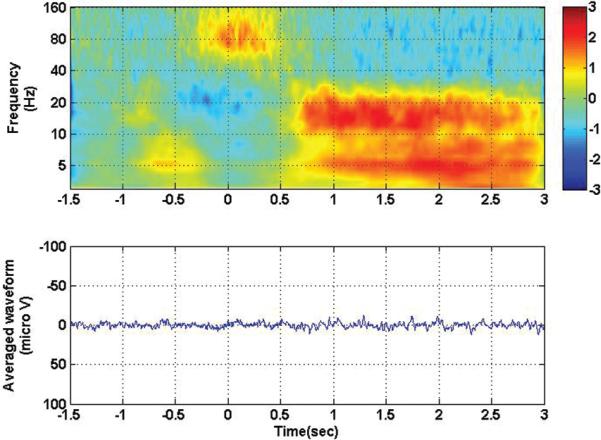
Fig. 3.
Time-frequency analysis (upper) and averaged evoked potential (lower) for contact 105, with all contralateral movement conditions collapsed together. Zero corresponds to movement onset. Note the disappearance of the visual evoked potential but the persistence of the high-frequency/low-frequency inversion that occurs during movement (at the zero time point).