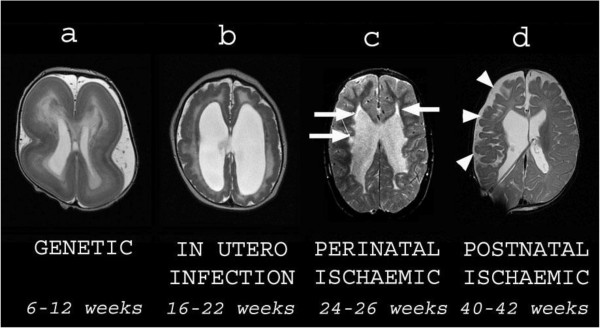
Figure 2.
Examples of different types of structural brain abnormalities in cerebral palsy All images are axial T2-weighted MRI scans. Each image is subtitled by its presumed aetiology and timing during gestation. a is a child with lissencephaly showing cortical thickening and agyria. b is a child with congenital cytomegalovirus infection showing an overfolded cortex (polymicrogyria), thin white matter and dilated lateral ventricles. c is an ex premature child showing cystic white matter injury (arrows) consistent with periventricular leukomalacia. d is a child who suffered a haemorrhagic stroke in the newborn period. There is cortical and white matter loss in the right frontal and parietal lobes (arrowheads) consistent with previous ischaemia.