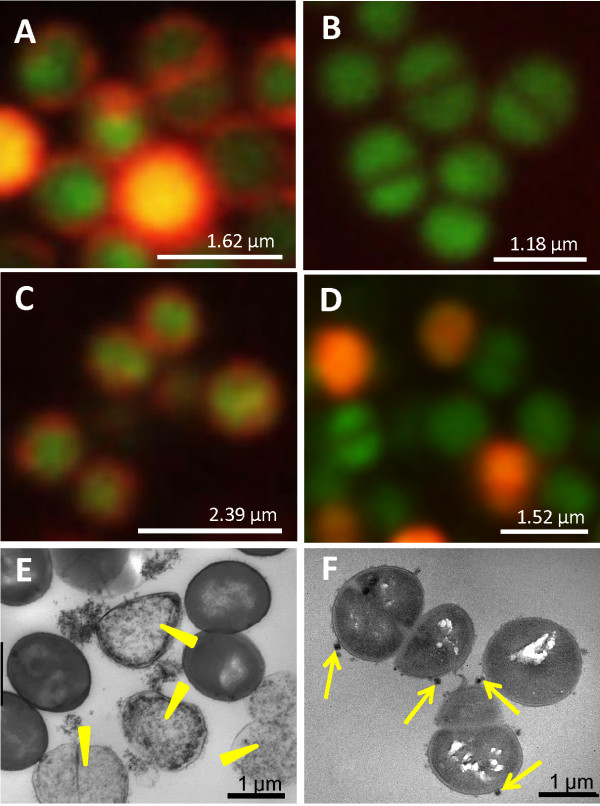
Figure 1.
Validation of bacterial cell labeling with iron oxide particles. Fluorescence microscopy of S. aureus bacteria (strain 6850) labeled with Syto 9 (green) and rhodamine-labeled 5-nm citrate-coated iron oxide nano particles (IONPs) (red) using different labeling strategies: (A) electroporation of electro-competent bacterial cells, (B) incubation of unmodified bacterial cells and (C) incubation of electro-competent bacterial cells. Syto 9 was used for co-registration. (D) S. aureus bacteria labeled with 5-nm amine-coated IONPs by incubation of electro-competent bacterial cells. Electron microscopy images of S. aureus bacterial cell samples labeled by (E) electroporation and (F) incubation show a high percentage of cell debris when the electroporation technique was used (yellow arrowheads in (E)) and clusters of IONPs bound to the surface of intact bacteria (yellow arrows in (F)).