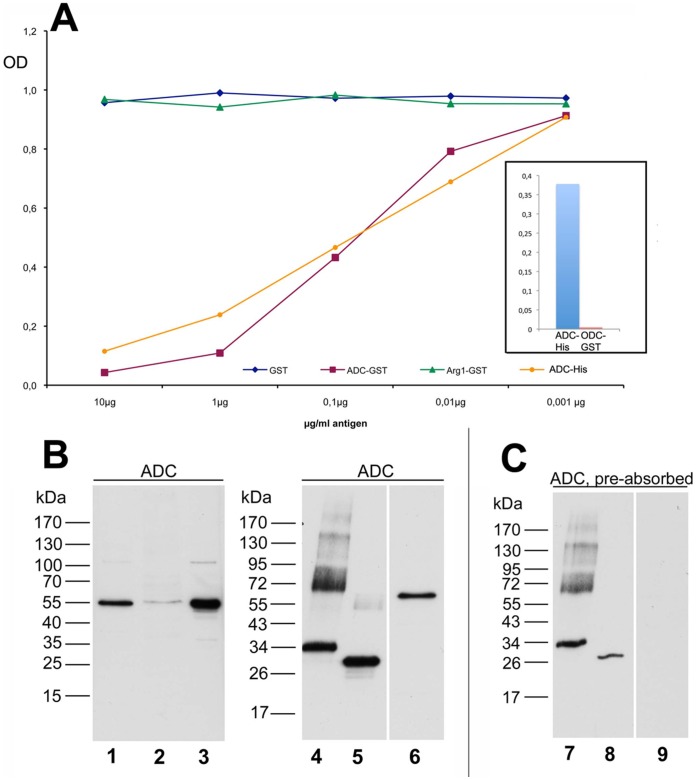
Figure 1. Characterization of the anti-ADC antibody.
A ELISA assay displaying anti-ADC activity. In a competitive ELISA assay preincubation with ADC-GST and ADC-His fusion proteins at increasing concentrations competitively inhibited the specific interaction, demonstrating the reactivity of the antibody against ADC fusion protein. In contrast, pre-adsorption using the unrelated fusion protein (Arg1-GST) or GST did not show any effect on immunoreactivity. The inset shows a direct ELISA, illustrating the activity of the anti-ADC antibody against the immunogen ADC as compared to a potentially cross-reacting ODC partial fusion protein. At the same dilution as used for the competitive assay (1∶30.000), no cross-reactivity was observed. B-C Characterization of the anti-ADC antibody by Western blotting. B: Strong protein bands at 55 kDa were detected in rat liver (lane 1 and 6) as well as in rat prostate tissue (lane 3). In rat brain (lane 2), at the same molecular weight a faint but distinct band was observed. Moreover, the antibody strongly reacted with the bacterially expressed partial fusion proteins ADC-GST (36,7 kDa, lane 4) as well as ADC-His (30,7 kDa, lane 5). C: Pre-absorption of the antibody with 10 µg/ml ADC-His purified fusion protein clearly attenuated the intensity of the fusion protein bands (lane 7, 8) and led to a complete disappearance of the ADC signal in rat liver homogenate (lane 9), thus demonstrating the specificity of the antibody. Loading: Lane 1, rat liver homogenate (25 µg); lane 2, rat total brain homogenate (50 µg); lane 3, rat prostate homogenate (25 µg); lane 4 and 7, ADC-GST fusion protein (25 ng); lane 5 and 8, ADC-His fusion protein; lane 6 and 9, rat liver homogenate (25 µg).