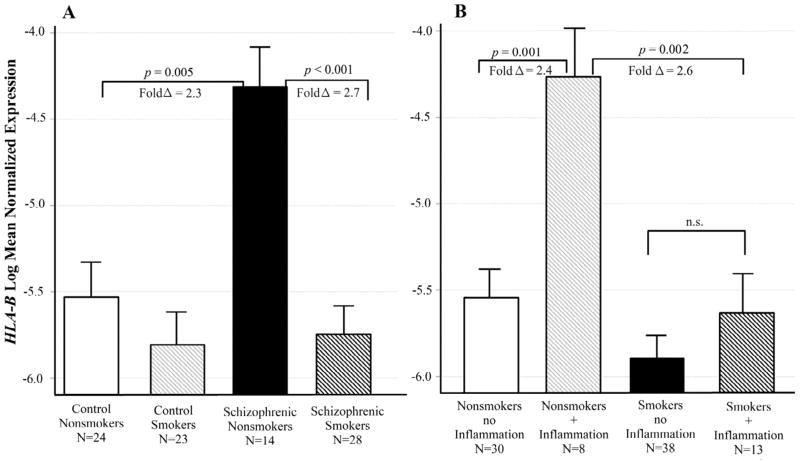
Figure 3. Interactive effects of schizophrenia, smoking and inflammatory illness on HLA-B expression.
Least squares means of log transformed expression relative to GAPDH. Means are adjusted for all other effects in the model. A. Schizophrenic nonsmokers had significantly increased HLA-B expression compared Control nonsmokers [F (1,87)= 10.69; p = 0.005; fold Δ = 2.3], and compared to schizophrenic smokers [F(1,87) = 22.99; p < 0.001; fold Δ = 2.7]. B. Nonsmokers with an inflammatory illness had significantly increased HLA-B expression compared to those with no inflammatory illness [F(1,87) = 18.15; p = 0.001; fold Δ = 2.4]. This difference in expression did not occur in the smokers. Bars are one S.E.M.