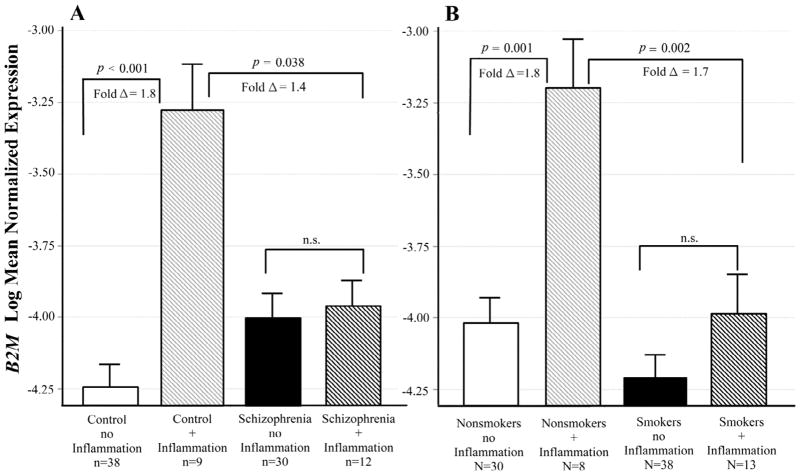
Figure 4. Interactive effects of schizophrenia, smoking and inflammatory illness on B2M expression.
Least squares means of log transformed expression relative to GAPDH. Means are adjusted for all other effects in the model. A. Controls with an inflammatory illness had significantly increased B2M expression compared to those with no inflammatory illness [F(1,87) = 24. 21; p < 0.001; fold Δ = 1.8]. This difference in expression did not occur in the schizophrenic subjects. B. Nonsmokers with an inflammatory illness had significantly increased B2M expression compared to those with no inflammatory illness [F(1,87) = 18.15; p = 0.001; fold Δ = 1.8). This difference in expression did not occur in the smokers. Bars are one S.E.M.