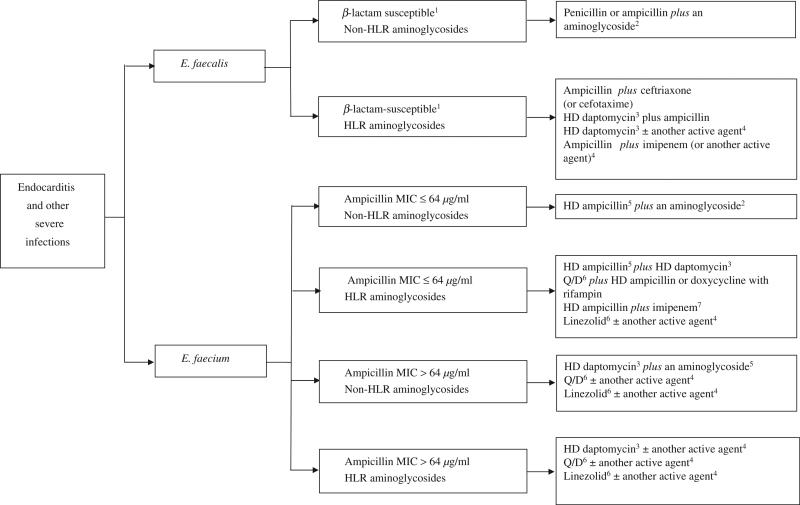
FIG. 1.
Suggested therapeutic alternatives in severe infections caused by vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infections. (1) In rare cases of β-lactamase-producing isolates, ampicillin-sulbactam (12–24 g/day) is suggested. The use of a continuous infusion is recommended by some experts. (2) Gentamicin or streptomycin. (3) Consider doses of 8–12 mg/kg day. (4) Agents with potential activity include tigecycline [62,63], doxycycline with rifampin or a fluoroquinolone (if susceptible to each agent). (5) Doses to up to 30 g/day could be considered. (6) Quinupristin-dalfopristin or linezolid are listed in the American Heart Association recommendations for the treatment of vancomycin and ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Linezolid has been used with success in a few cases of meningitis as a result of vancomycin-resistant enterococci [61,74]. (7) if imipenem MIC < 32 mg/L. HLR, high-level resistance; HD, high-dose.