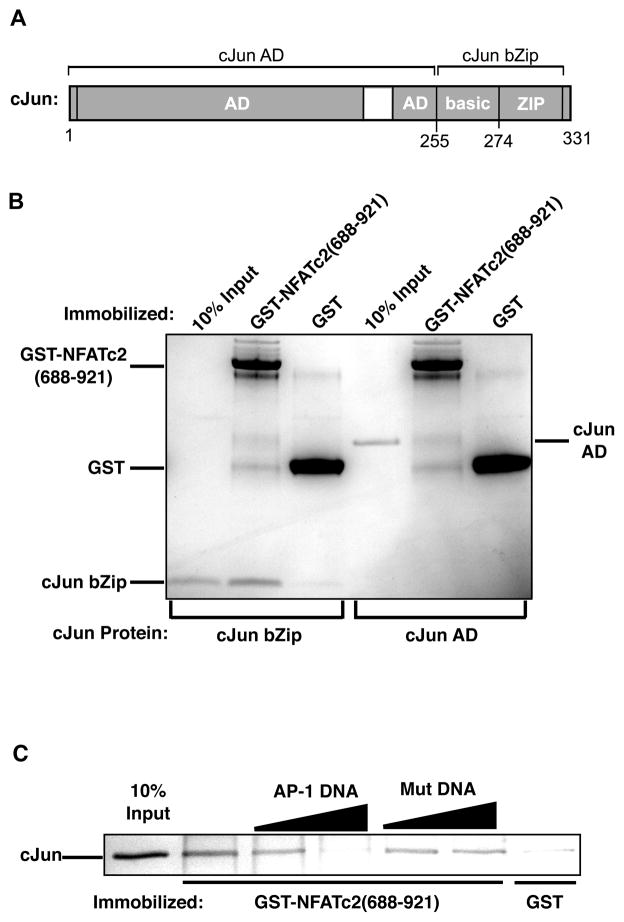
Figure 6.
The bZip domain of cJun is sufficient for binding the C-terminal activation domain of NFATc2 and binding is inhibited by AP-1 DNA. (A) Schematic of cJun showing the activation domain region (AD) and the bZip, which is responsible for dimerization and DNA binding. (B) The bZip domain of cJun is sufficient to bind the C-terminal activation domain of NFATc2. Proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and visualized with coomassie stain. (C)AP-1 DNA blocks the interaction between cJun and the C-terminal activation domain of NFATc2. GST-NFATc2(688-921) and control GST were immobilized and incubated with 15 pmol of purified cJun. AP-1 DNA or mutant DNA (10 or 20 pmol) were added to the reactions, bound cJun was resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver stain.