Fig. 1.
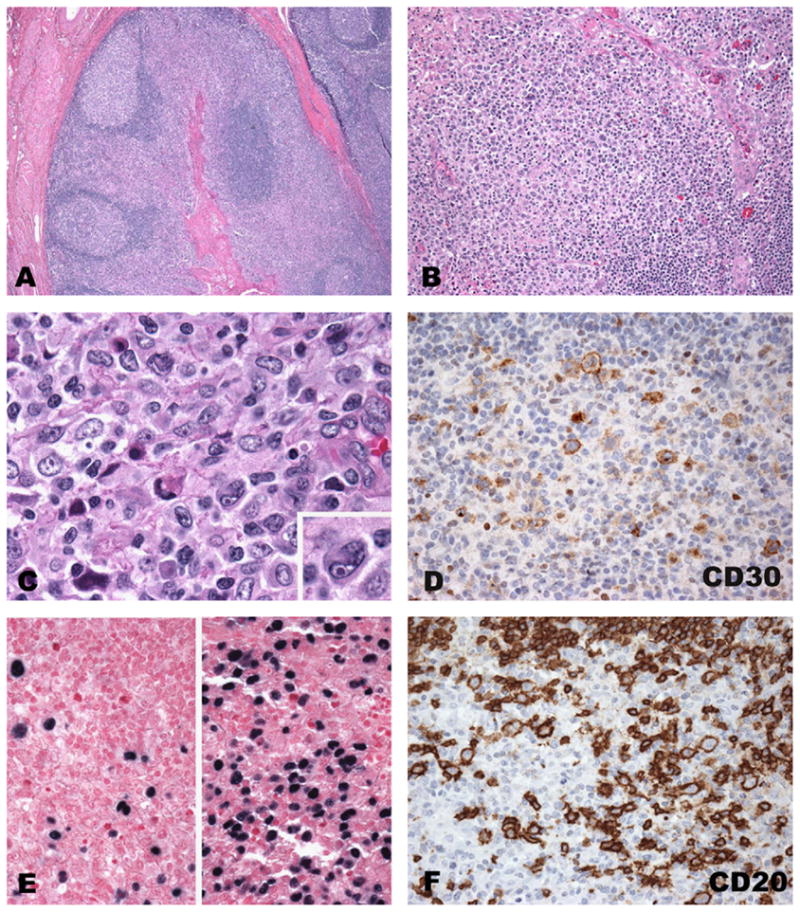
Acute infectious mononucleosis involving tonsils. (A) Low power revealing architectural preservation with reactive secondary B follicles and expanded interfollicular areas with a polymorphic cellular composition and focal necrosis (B and C). Large atypical cells with Reed–Sternberg-like features (inset C) are positive for CD30, EBV and CD30 (D–F). In situ hybridization for EBV (E) reveals a great variation in the number of positive cells and their size (separate fields, same tonsil).
