Figure 1.
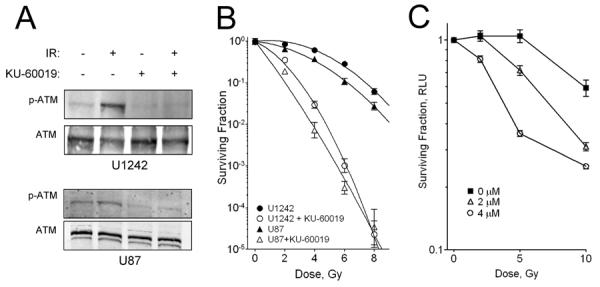
KU-60019 inhibits the ATM kinase and radiosensitizes human glioma cells in vitro. A, Western blotting. U1242 and U87 cells were exposed to 3 μM KU-60019 (−0.5 hr) or left untreated and then irradiated with 5 Gy or not and then processed at 0.5 hr for western blotting with anti-p(S1981)-ATM antibody and normalized to ATM protein with anti-ATM antibody. B, Survival assay. Human glioma U1242 and U87 cells were serially diluted, plated [plating efficiency: 0.20 (U87); 0.22 (U1242)], and exposed to KU-60019 (3 μM) or not and then irradiated with 2, 4, 6, or 8 Gy followed by radiosurvival colony-forming assay. Data points, surviving colonies plotted as fraction of control; error bars, SD; N ≥ 3. Where error bars are not seen they are obscured by symbols. At 8 Gy, KU-60019 radiosensitization of U87 and U1242 cells was highly significant (P < 0.0001). Dose-enhancement ratios - U1242: 3.2; U87: 3.0. Radiobiological parameters - U87 α/β ratio: 11.7 Gy; U87 + KU-60019: 34.8 Gy; U1242: 1.8 Gy; U1242 + KU-60019: 3.4 Gy. C. Survival assay of mouse glioma stem cells. Cells were grown as neurospheres, trypsinized, and seeded in quadruplicate in a microtiter plate followed by exposure to KU-60019 and radiation as described in the Materials and Methods. At 10 Gy, KU-60019 radiosensitization was highly significant (P < 0.0001).
