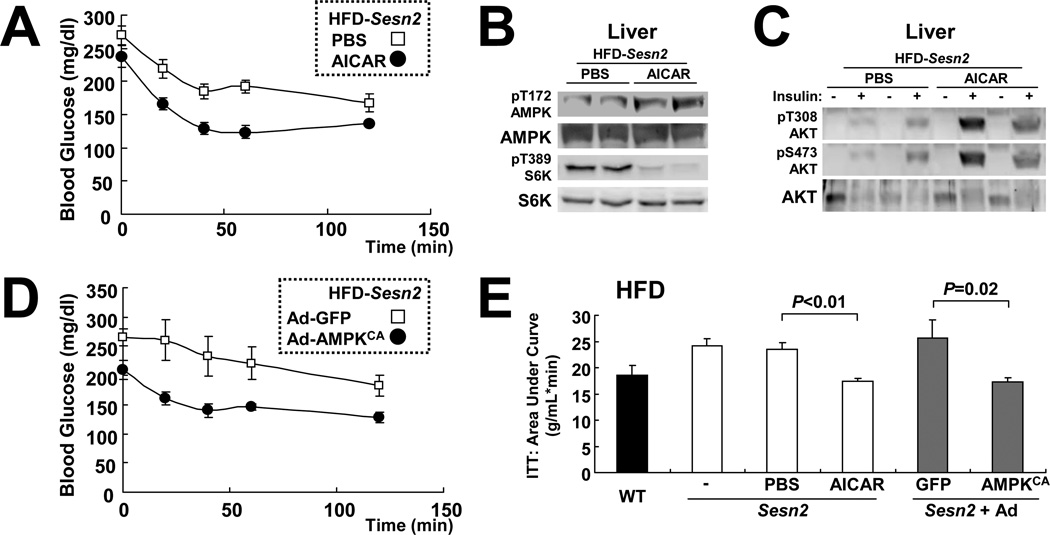
Figure 4. Reactivation of hepatic AMPK restores insulin resistance of HFD-fed Sesn2−/− mice.
(A) Sesn2−/− mice kept on HFD for 3 months were subjected to daily i.p. injection of 250 mg/kg body weight AICAR or vehicle (PBS) for 5 days. After 6 hrs of fasting, the mice were subjected to ITT (n=6). (B and C) After 10 days of AICAR or vehicle (PBS) injection, livers from the mice described above were collected after 6 hrs of fasting, before (B and (−) in C) or 10 min after ((+) in C) insulin injection (0.8 U/kg body weight). The livers were analyzed for protein phosphorylation and expression with the indicated antibodies. (D) Sesn2−/− mice kept on HFD for 3 months were infected with adenoviruses expressing GFP (Ad-GFP) or constitutively active AMPK (Ad-AMPKCA). After 6 hrs of fasting, ITT (n=6) was performed at 24 hrs after infection. (E) Area-under-curve analysis of ITT data. Values from untreated Sesn2+/+ (WT) and Sesn2−/− (−) mice of the same HFD cohorts were provided as reference (n≥6). Data are presented as means ± standard error. P values were calculated using Student’s t-test.