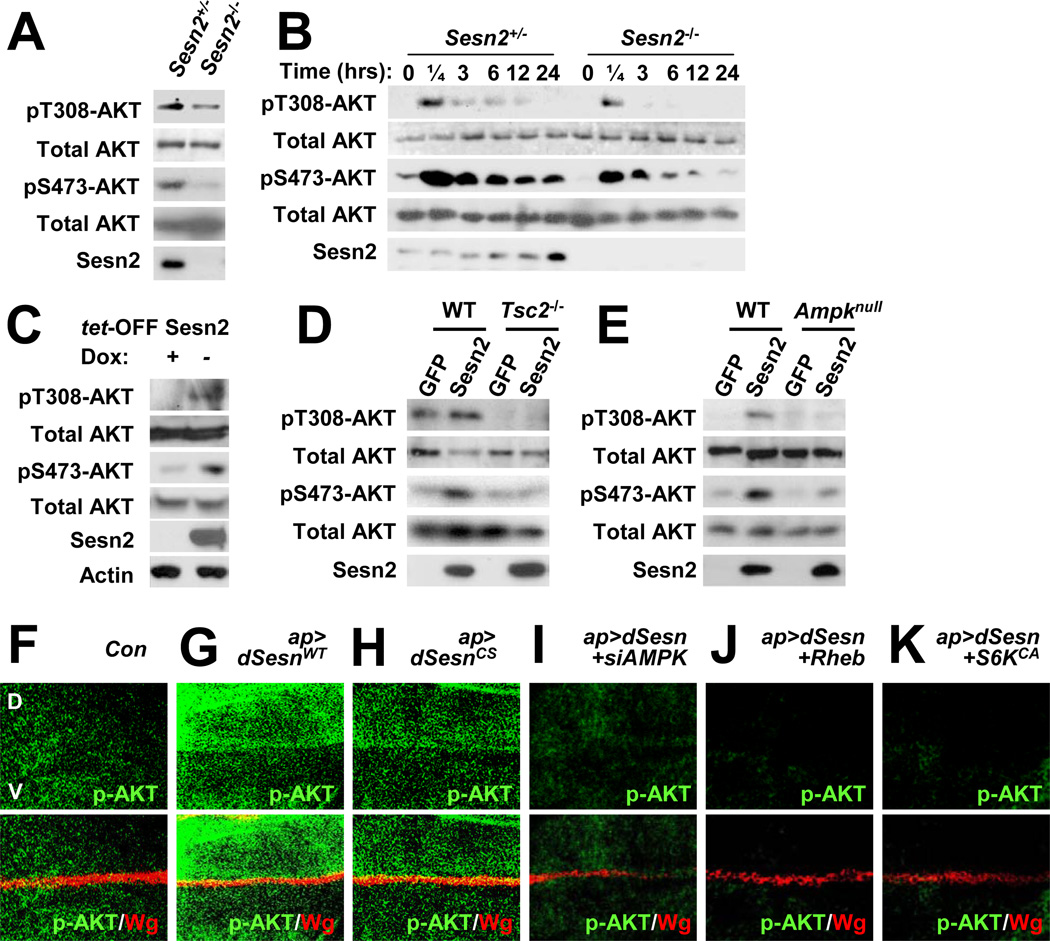
Figure 7. Sestrin2 potentiates AKT signaling through the AMPK-TSC2 axis.
(A) Reduced AKT phosphorylation in Sesn2−/− MEFs. Steady state AKT phosphorylation at Thr308 and Ser473 in MEFs grown in the presence of 10% FCS was examined by immunoblotting. (B) Reduced insulin-stimulated AKT phosphorylation in Sesn2−/− MEFs. After 24 hrs of serum starvation, MEFs were collected at the indicated times after insulin treatment and analyzed for AKT phosphorylation. (C) Sestrin2 stimulates AKT signaling. Flag-tagged Sestrin2 was induced in MCF7-tet OFF Sesn2F cells by doxycycline (Dox) removal (−). Control cultures were left with Dox (+). Cell lysates prepared after 24 hrs were analyzed for expression and phosphorylation of the indicated proteins. (D and E) Sestrin2 activation of AKT is TSC2 and AMPK dependent. WT, Tsc2−/− or Ampkα1−/−/Ampkα2−/− (Ampknull) MEFs were infected with lentiviral vectors encoding GFP or Flag-tagged Sestrin2 (Sesn2). Protein phosphorylation and expression were examined at 48 hrs post infection by immunoblotting. (F–K) Activation of AKT by dSestrin in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. Larval wing discs of the indicated strains were stained to visualize AKT phosphorylation at Ser505 (p-AKT, equivalent to Ser473 in mice). The dorsal side points upwards. Dorsoventral boundary (D/V in F) was visualized by staining with an antibody to the wingless protein (Wg). Indicated transgenic elements were overexpressed only in the dorsal compartment as described (Lee et al., 2010).