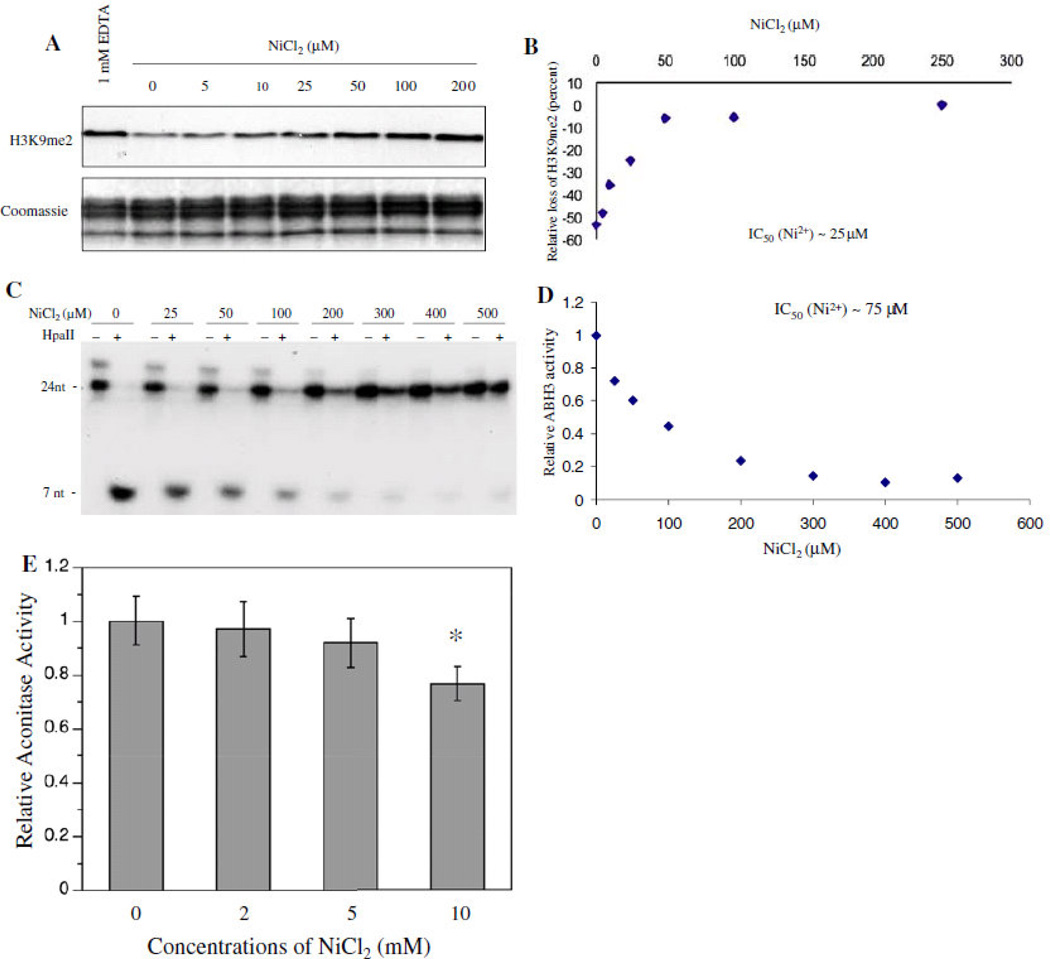
Figure 5.
A kinetic study on Ni inhibition of JHDM2A and ABH3 demethylase activity. (a) Purified Flag- JHDM2A was assayed for its demethylase activity in the presence of different concentrations of Ni(II) ions as indicated. The assay with addition of EDTA, a chelator of divalent metals, was performed in parallel as a negative control. (a) Data quantification of (a). (c) Purified 69His-tagged ABH3 was assayed for its demethylase activity in the presence of different concentrations of Ni(II) ions as indicated. (d) Data quantification of (c). (e) Purified aconitase, an Fe–S cluster-containing enzyme, was incubated with different concentrations of Ni(II) ions for 4 h. After incubation, the aconitase activity was measured immediately as previously described. Aconitase activity is presented as that relative to levels in the control samples. Each bar represents the mean (±SD) from three samples per treatment. *Statistically significant change (P<0.05) compared to control samples. From “Iron- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent Dioxygenases:an emerging group of molecular targets for nickel toxicity and carcinogenicity” vol. 22 by Chen H. and Costa M. Copyright 2009 by Biometals. Reproduced with permission of Biometals via Copyright Clearance Center