Fig. 2.
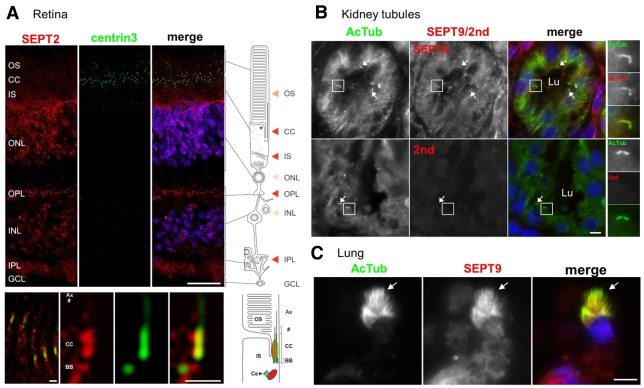
Septins localize to the axoneme of cilia in vivo. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence triple staining of SEPT2 (red), centrin isoform 3 (green), which was used as marker for the connecting cilium (CC), basal body and the adjacent centriole (Ce), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). In the human retina, SEPT2 is localized in the outer segment (OS), the inner segment (IS) and the synaptic compartments of the outer (OPL) and inner (IPL) plexiform layer. Additional weak staining was detected in the nuclei of the outer (ONL) and inner nuclear layer (INL). The bottom panel shows high magnification indirect immunofluorescence of SEPT2 (red) and centrin3 (green) in longitudinal cryosections through human photoreceptor cells. The high magnification reveals SEPT2 localization as a fibrous pattern in the inner and outer segment. Merged images reveals partial colocalization of SEPT2 with centrin3 at the centriole, the basal body (BB) and along the connecting cilium. Scale bars: top, 25 µm; bottom, 1 µm. (B) Tissue sections from adult human kidney were stained with antibodies against AcTub (red) and either SEPT9 (green) or with secondary anti-rabbit antibodies only (2nd; green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Representative tubule lumens are indicated (Lu). Higher magnifications of representative cilia are shown on the right, and other cilia are identified with white arrows. Scale bar: 5 µm. (C) Tissue sections from the lung of a 33-week fetus were stained with antibodies against AcTub (red) and SEPT9 (green). White arrows point to a representative ciliary tuft. Scale bar: 5 µm.