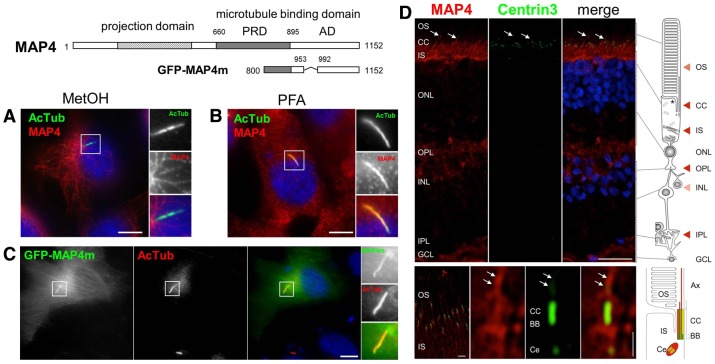
Fig. 7.
MAP4 localizes to the primary cilium in RPE1 cells. Schematic representation of MAP4 showing its functional domains and the region encoded by the GFP-MAP4m fusion. PRD, proline-rich domain; AD, affinity domain. (A,B) RPE1 cells were grown on coverslips, serum-starved for 48 hours and then fixed with methanol (MetOH; A) or paraformaldehyde (PFA; B) then processed for immunofluorescence using anti-acetylated tubulin (AcTub, green) and anti-MAP4 (red) antibodies, and DAPI (blue) to stain nuclei. (C) RPE1 cells were transiently transfected with the GFP-MAP4m encoding plasmid, fixed and processed for immunofluorescence using an antibody against acetylated-tubulin (red) and DAPI (blue) to stain nuclei. Panels on the right are enlarged views of representative cilia (boxed in the main images). Scale bars: 5 µm (A–C). (D) Indirect immunofluorescence staining of MAP4 (red), centrin3 (green), used as marker for the connecting cilium (CC), basal body and the adjacent centriole (Ce), and the nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). In the human retina MAP4 is localized in the outer segment (OS) and in the inner segment (IS) of the outer plexiform layer (OPL). Bottom panel shows high magnification indirect immunofluorescence of MAP4 (red) and centrin3 (green) in longitudinal cryosections through human photoreceptor cells. Merged images reveal partial colocalization of MAP4 with centrin3 at the centriole, the basal body (BB) and along the connecting cilium and axoneme (white arrows). Scale bars: top, 25 µm; bottom, 1 µm.