Fig. 1.
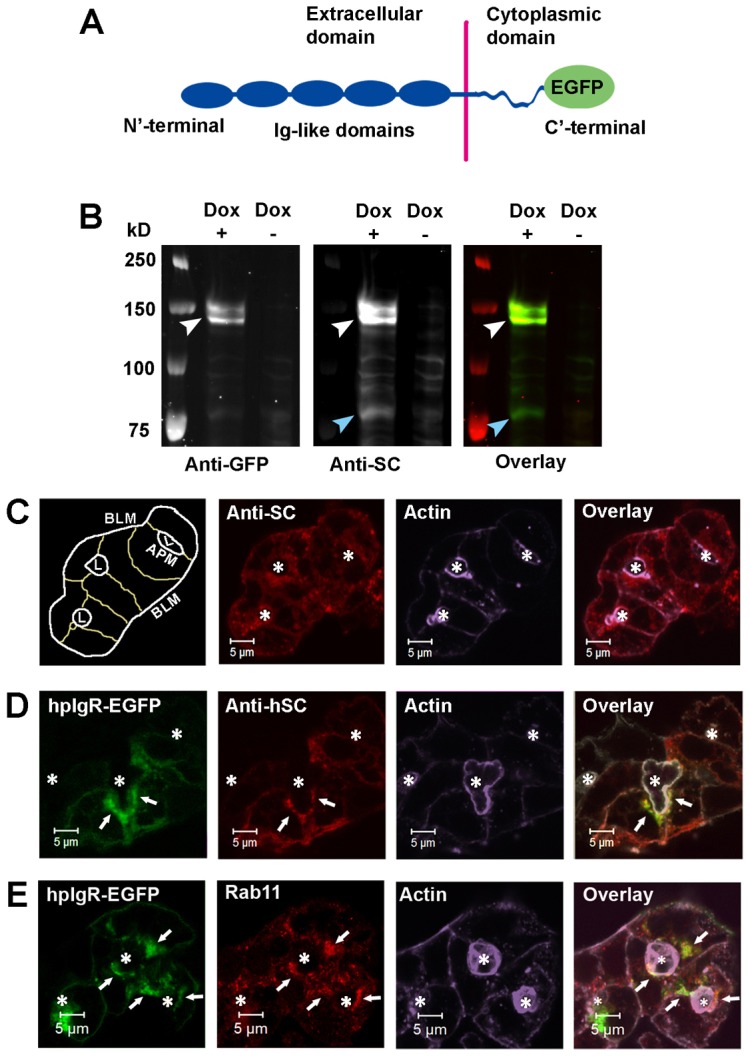
Characterization of the hpIgR construct. (A) Schematic of the hpIgR-EGFP construct showing EGFP fusion to the C′-terminal cytoplasmic domain of hpIgR. (B) LGACs were co-transduced with Ad hpIgR-EGFP and Adeno-X Tet-On®. After induction with 0.1 µg/ml doxycycline (+) or not (−) overnight, cells were lysed with non-denaturing lysis buffer. Lysate was pre-cleared as in the Materials and Methods, and analyzed by western blotting using primary goat anti-hSC or mouse anti-GFP antibodies, as well as secondary IRDye®800-conjugated donkey anti-goat or IRDye®700-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibodies, respectively. White arrowhead, hpIgR-EGFP; blue arrowhead, SC. (C,D) Non-transduced LGACs (C) or LGACs expressing hpIgR-EGFP (D) were fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with primary goat anti-hSC antibody, as well as secondary Alexa Fluor®-568-conjugated donkey anti-goat antibody and Alexa Fluor®-647-conjugated phalloidin. (E) LGACs expressing hpIgR-EGFP were fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with primary mouse anti-Rab11 antibody, secondary Alexa Fluor®-568-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody and Alexa Fluor®-647-conjugated phalloidin. White arrows, colocalization between red and green; *, lumena. Scale bars: 5 µm.
