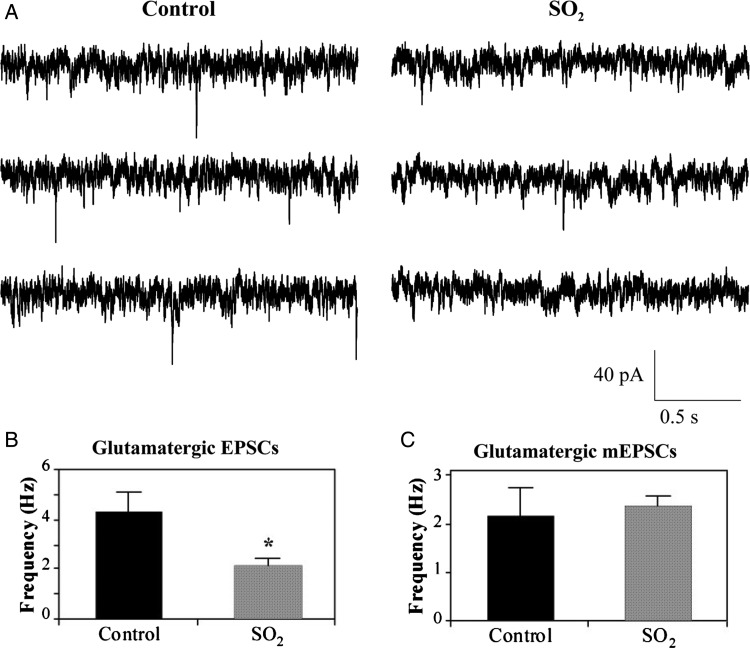
Figure 4.
Spontaneous glutamatergic EPSCs (A) were isolated and recorded from labelled CVNs in the nucleus ambiguus using the whole-cell patch-clamp configuration. Representative traces shown are from three consecutive time periods recorded from one control and one SO2-exposed pup, as labelled. EPSC frequency was significantly decreased by 51.2% following perinatal SO2 exposure (2.1 ± 0.3 Hz, n = 11 animals) compared with control pups (4.3 ± 0.8 Hz, n = 5 animals), as shown in (B). Bath application of tetrodotoxin (TTX), a voltage-gated Na+-channel antagonist, was used to record glutamatergic miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs). mEPSC frequency in control (2.1 ± 0.6 Hz, n = 5 animals) and SO2-exposed animals (2.3 ± 0.2 Hz, n = 6 animals) were not significantly different (*P < 0.05).