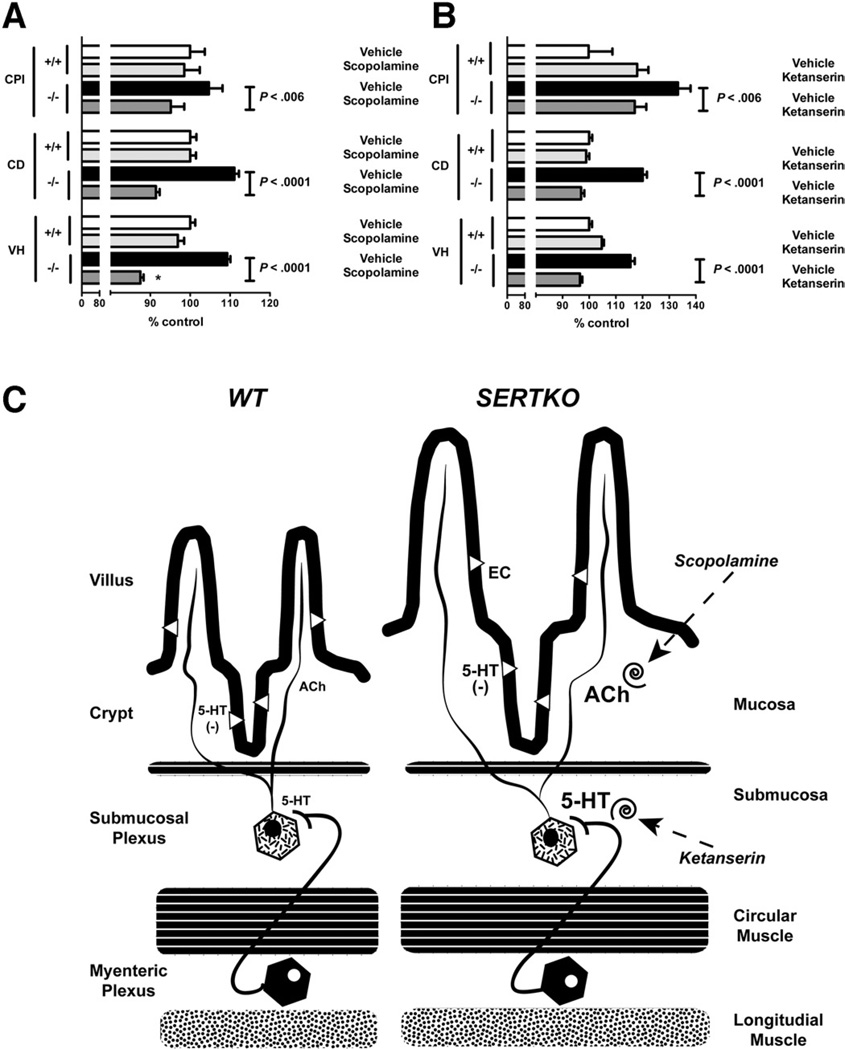
Figure 6.
(A) VH, CD, and CPI are all significantly shorter in SERTKO mice treated with scopolamine than with vehicle. VH, CD, and CPI were quantified and expressed as the percentage of control (WT + vehicle). (B) VH, CD, and the CPI are all significantly shorter in SERTKO mice treated with ketanserin than with vehicle. (C) A hypothetical explanation of the mucosal changes seen in SERTKO mice. The deletion of SERT amplifies the effects of 5-HT that neurons secrete. Serotonergic stimulation of 5-HT2A–receptor– expressing cholinergic neurons in submucosal ganglia causes release of ACh in the mucosa, which stimulates epithelial growth. Blocking muscarinic receptors with scopolamine or 5-HT2A receptors with ketanserin thus prevent SERTKO-associated mucosal growth.