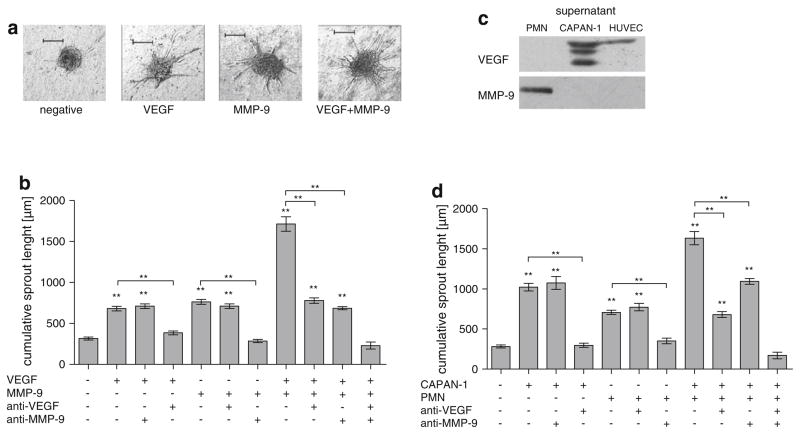
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the angiogenic effect of PDAC tumor cells, VEGF, granulocytes and MMP-9. Quantitative three-dimensional in vitro angiogenesis assay. Capillary sprouting originating from the spheroids was quantified. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) have a low baseline level of capillary sprouting. Representatives are shown in a from left to right: control HUVEC, HUVEC + VEGF (10 ng/ml), HUVEC + MMP-9 (0.1 ng/ml), HU-VEC + VEGF (10 ng/ml) + MMP-9 (0.1 ng/ml). b The effect of VEGF and MMP-9 is additive (P < 0.001, compared to VEGF or MMP-9 alone). Antibodies to VEGF or MMP-9 (10 μg/ml each) inhibit the specific stimulus induced by VEGF or MMP-9 but not vice versa (P < 0.001 compared to corresponding control). c Quantitative Western blot analysis of CAPAN-1, PMN and HUVEC culture supernatants for VEGF and MMP-9. After 72 h of culture in FCS free medium, HUVEC, PMN and CAPAN-1 supernatants were quantified by SDS–PAGE and Western Blot. MMP-9 was only found only in the PMN supernatant whereas VEGF was identified in the CAPAN-1 and HUVEC supernatants. d The effect of PMN and CAPAN-1 cells is additive (P < 0.001, compared to CAPAN-1 or PMN alone). Antibodies to VEGF or MMP-9 (10 μg/ml each) inhibit the specific stimulus induced by CAPAN-1 or PMN but not vice versa (P < 0.001 compared to corresponding control). Error bars: SEM; **: P < 0.001. To avoid overcrowding of the graphs, not all P values are denoted, please see Results section