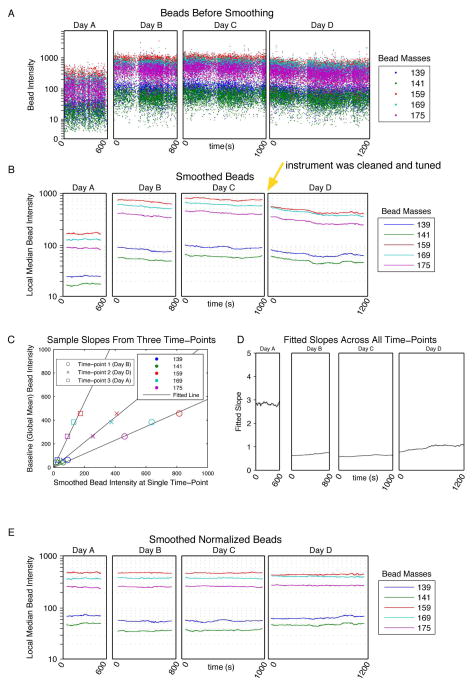
Figure 2. Bead smoothing and normalization.
(A) The raw intensities of the bead events in all of the bead channels were plotted over time for four files acquired on different days. (B) Smoothed intensity values were calculated by computing the median intensities across a sliding window of 500 beads. The smoothed intensities of the bead events in all of the bead channels were then plotted over time in the four files. Between collection of data files 3 and 4 the instrument was cleaned and tuned (yellow arrow), which resulted a shift in the relative bead intensities. (C) At each time-point in the smoothed data, the slope of the line through the origin was determined by minimizing the sum of the squared error between the bead intensities at that time point and the mean smoothed bead intensities across the experiment. The fits at three time points are shown. (D) The fitted slopes for all time points across the experiment. (E) The raw bead intensities were multiplied by the fitted slopes at each time point and then re-smoothed and plotted.